Search the Community
Showing results for 'tv'.
-
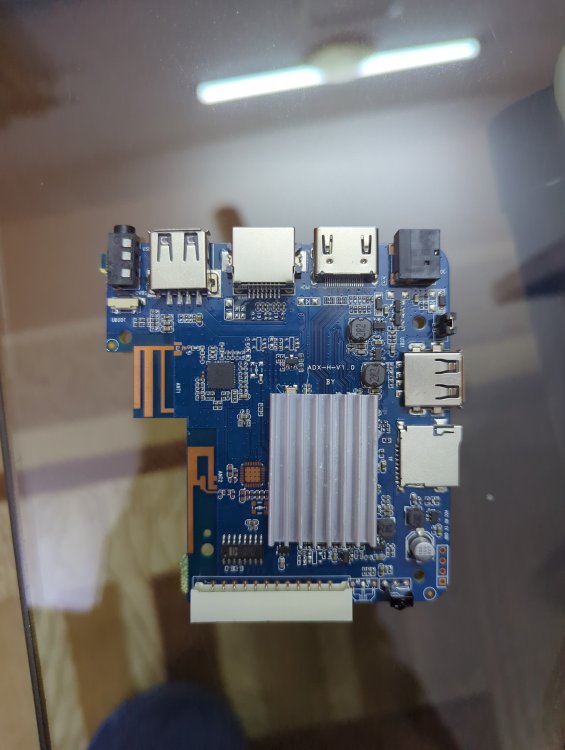
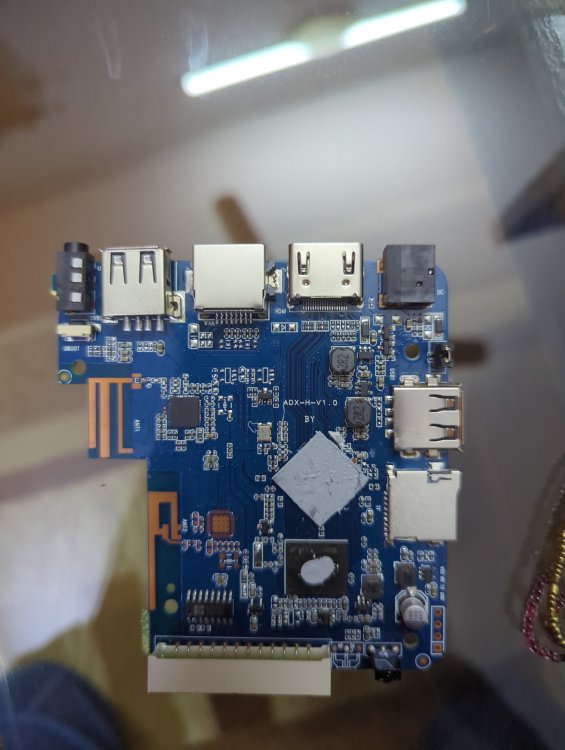
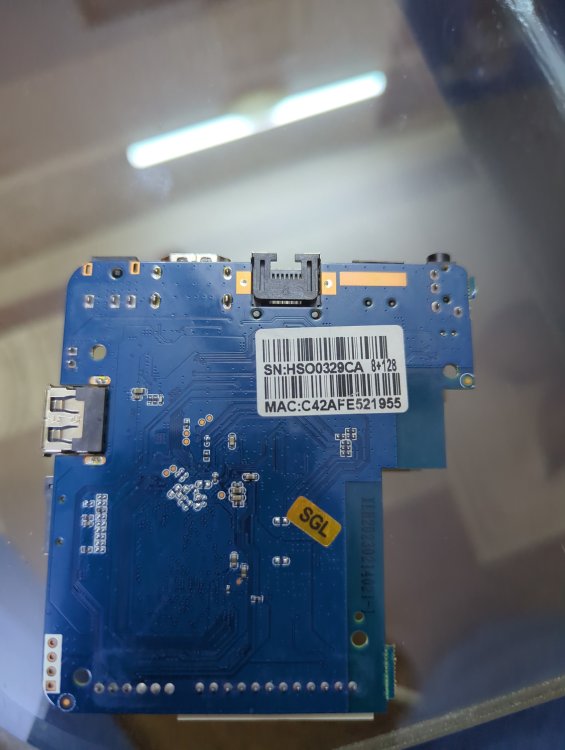
Basically it has 1 gb ROM 8gb ram h3 chip and I HAVE put many img files on SD card NONE of them boot and as soon as I take the SD card out it boots into android perfectly fine... I'm lost on words and what to do I have also tried FEL mode on linux but the request times out with error -7 power supply is 5v 2a which is fine for this so not that and I'm using a 256gb a1 rated SD card. This is from a generic Chinese tv box called meecom and it has ADX-H-V1.0 written on it. I also changed the dtb files a lot but it still gave no display or sign that it was booted into armbian idk what to do help ( btw I repasted it that's why it has no thermal putty on it)
-
Hi all, I’m working with an Amlogic S805X (P241) board and I’d like to run Armbian on it, but I need a kernel 5.15 LTS build that boots reliably (especially from USB/SD). I see Armbian community builds with kernel 6.x for Amlogic TV boxes (e.g., Armbian_community_26.x), but these do not boot successfully on my P241. I previously successfully booted Armbian with kernel 5.9, but I want an image based on the 5.15 LTS kernel if possible. Is there an existing downloadable image for S805X/P241 with kernel 5.15? If not, can you share build parameters (BOARD=, BRANCH=, kernel target) to compile a minimal Armbian image with 5.15 that uses meson-gxl-s805x-p241.dtb? I also want to confirm the correct dtb file and boot configuration needed. Kernel 6.x gives me reserved-memory / CMA errors on S805X P241 and didnt boot Kernel 5.x booted , Is there any 5.15 LTS Armbian image, or how can I build one? Thanks!
-
There are no Armbian builds that old, in fact Amlogic TV boxes weren't incorporated into Armbian until later Linux kernels. What you must have been using would most likely have been a fork of Armbian. What you are asking for isnt possible in the way you are asking. You essentially want Armbian ported to the 5.15 Linux kernels, which is a huge project. You would be better served but spending a month or so figuring out why current kernels don't work for you and fixing that.
-
Hello averyone I'm trying to download the multitool.img.xz can someone please help me find it or share a valide link?
-
I recently got this tv box emulator thing but i now emulate games on my laptop for convineince. I decide to download armbian on the tv box so that i can set up pi-hole for network wide ad blocking. Ive tried multiple times but i cant see to get it working. Cpu: Amologic S905L Ram:2 gig DDr3 ive been downloading this version https://github.com/ophub/amlogic-s9xxx-armbian/releases/download/Armbian_jammy_arm64_server_2026.02/Armbian_26.02.0_amlogic_s905l_jammy_6.1.161_server_2026.02.02.img.gz been using this dtb meson-gxl-s905x-p212.dtb been using this u bootfile named: u-boot-s905x-s912 To reboot the system there is no button in the AV port and the box refuses to download any apk or app for terminal emulator, Developer tools are not available,threfore i prefer to do it through the update method. the file structure Ive been following these instructions from gemini https://gemini.google.com/share/1e335432197f https://gemini.google.com/share/0a6ce8a19d0c Please ask me if you need more info I also asked in reddit btw
-
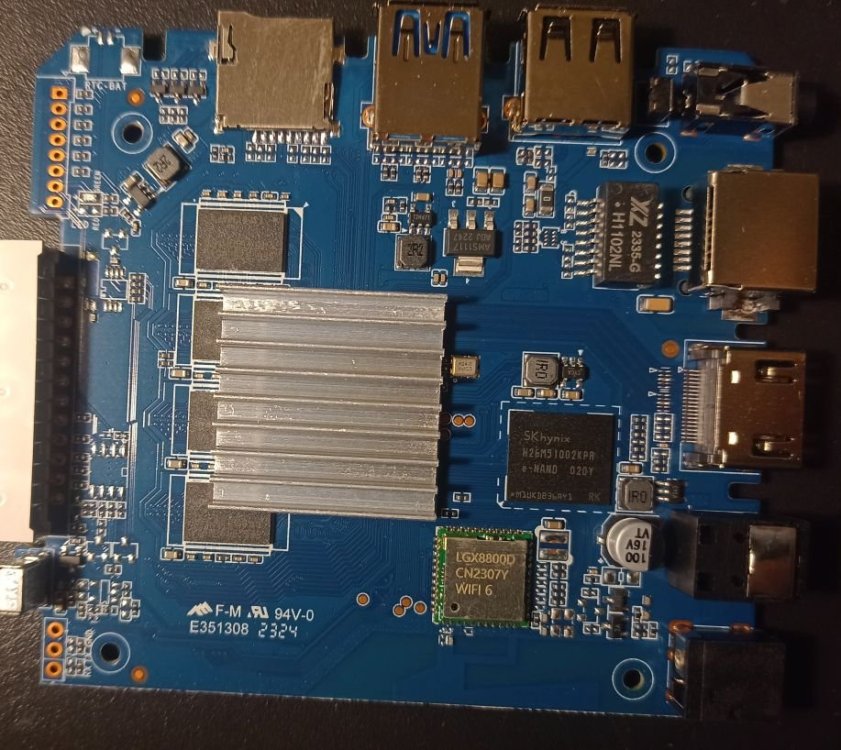
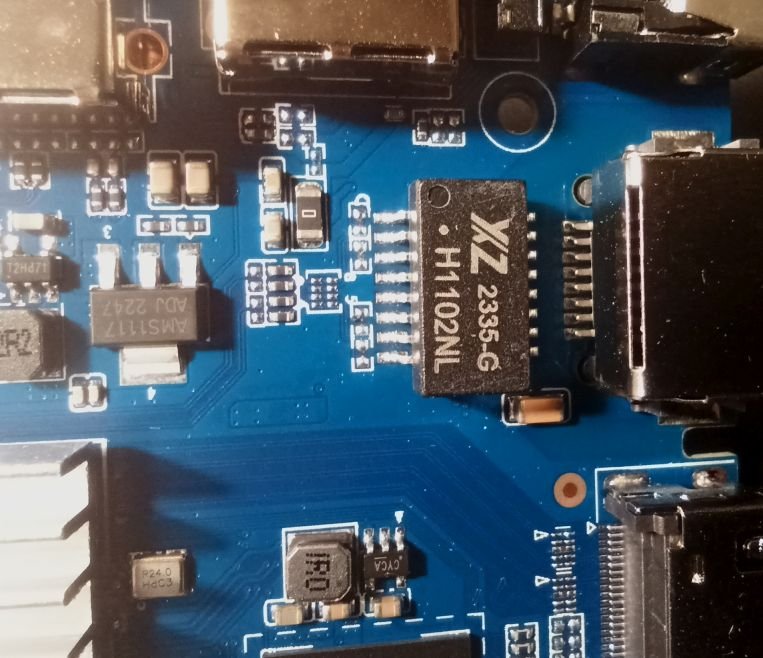
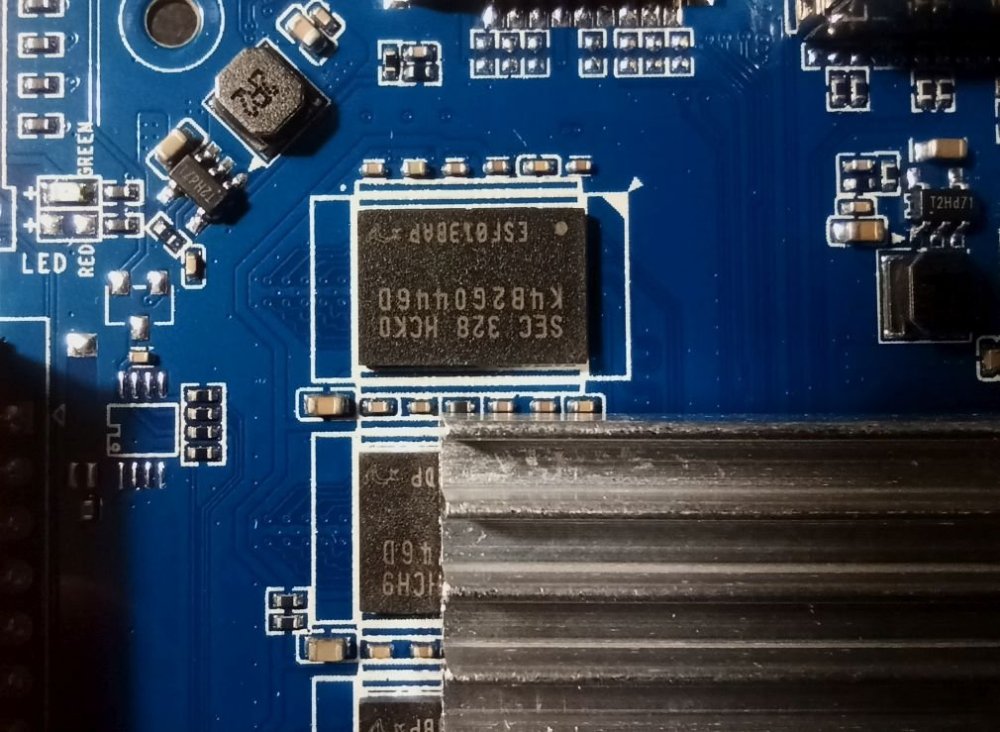
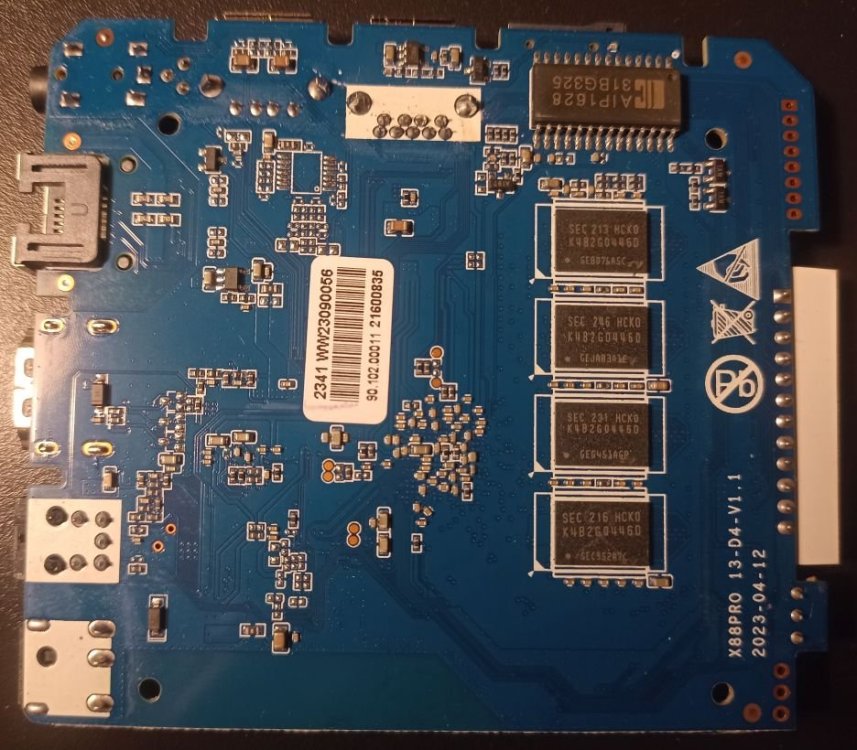
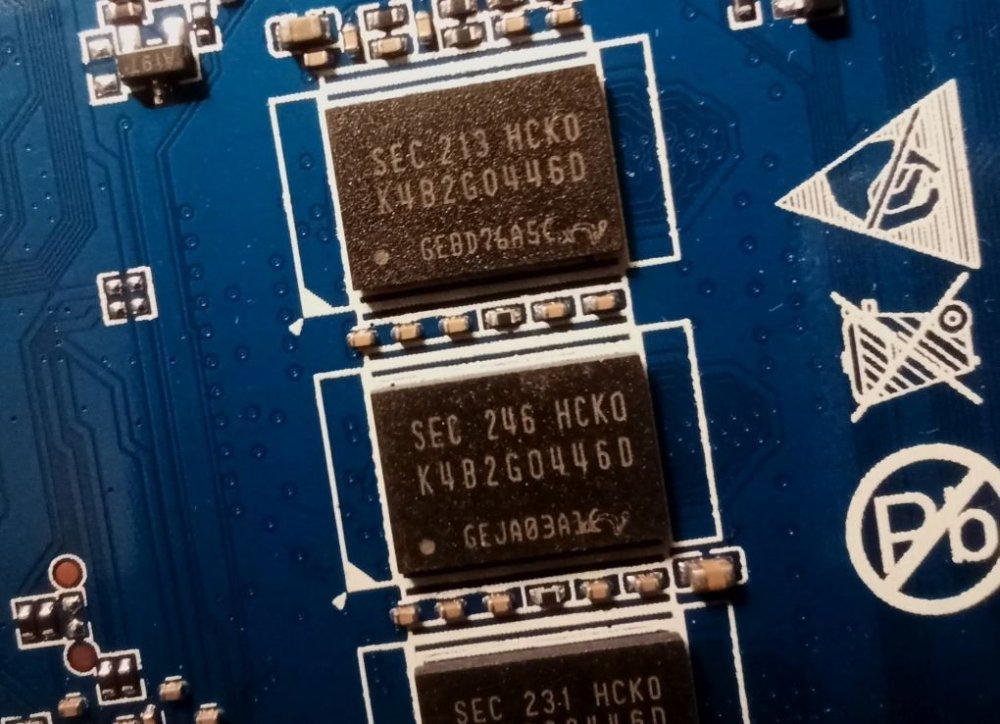
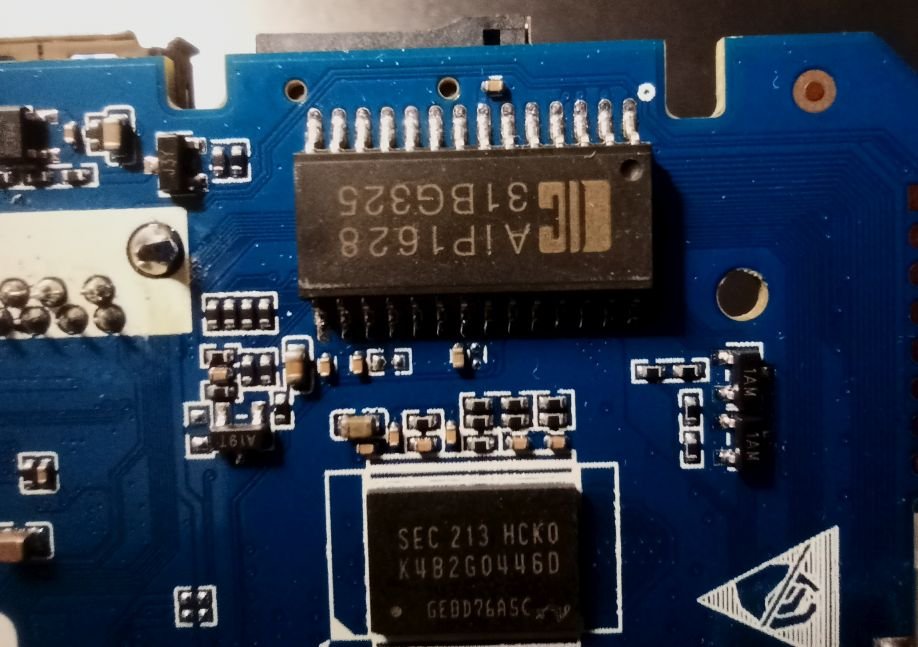
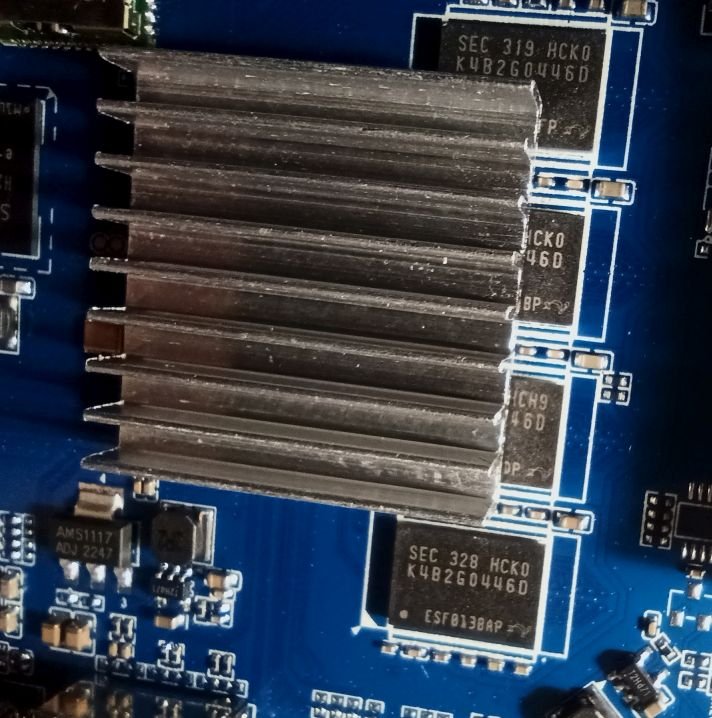
So I bought this chinise Android TV Box and would love to install armbian on it. I am new on this and discovered armbian just after buying it. I didn't know there was no support and not official open source for the Rockchip RK3528, otherwise I would have chosen any other. The box works fine but it has that known malware that send packets to suspicious links (I scanned activity with pi-hole). Description says it has 2GB RAM and 16GB storage (Hynix H26M51002KPR) WiFi chip is LGX8800D I attach images of the board and all of it's componentes, including IR sensor and display. It also has a red LED that turns on when in stand-by mode. I hope this help to develop or patch a working version of armbian for it. I have already read about some patches around that would probably work, but I' new to this and I'm not sure how to start. What I would like to do first is a completly ROM backup, and start doing test with a pendrive or SD card, not writting directly to the eMMC (if possible) until the important things get working. And any help would be appreciated. Edit: I will keep posting in this thread with my progress (or attemps!)
-
I currently have a TV box with @Nick A Armbian-unofficial_25.05.0-trunk_x98h_bookworm_edge_6.12.11_xfce_desktop.img. I have installed linux-headers-edge-sunxi64_25.05.0-trunk_arm64__6.12.11 from the same repository. I'm trying to build a custom module to get the LCD working but I keep coming up against a Exec Format Error which implies a mismatch between the build version and the installed version. But I can't find the cause. I have been following the build instructions for tm16xx-display which hasn't been a smooth process. I've had to remove some forward slashes in the Makefile so it would find the drivers/auxdisplay folder and the line-display.mod.c file it created had entries with multiple double quotes that caused errors. I had to change ""LINEDISP"" to "'LINEDISP'" before it would build. I should also mention I have previously tried OpenVFD and come up with the exact same issue so I don't think it's related to tm16xx. uname - r 6.12.11-edge-sunxi64 Vermagic of the module 6.12.11-edge-sunxi64 SMP preempt mod_unload aarch64 uname -a Linux x98h 6.12.11-edge-sunxi64 #1 SMP PREEMPT Thu Jan 23 11:23:05 EST 2025 aarch64 GNU/LINUX I have little experience with building things in Linux. Am I missing something simple? Is "PREEMPT" listed in all caps in uname -a an issue when the vermagic line is lower case? What about mod_unload? Any other ideas? I've been googling all day and got nowhere. Most results show different version between uname and vermagic which isn't the case here as far as I can tell. I guess I just need to know if it's possible to build custom modules with armbian images or if it's something that just doesn't work and I should forget about it. Thanks.
-
i have an android tv box. model name: tx 10 pro. i want to install ARMbian on it. there is a reset button under the av port. it has 2 gb of ram and 4 gb of rom (though the internet says 8G ram and 128G rom, also the android ui too). i have enabled both usb debugging and oem unlocking from the android developer option menu. the tv box can go to recovery mode using adb command. until going to the recovery mode, the adb connects perfectly but whenever it goes into recovery mode, the adb cant connect to the tv box. it consists option for fastboot inside the recovery mode but whenever i try to apply any command (e.g. fastboot/adb) the tv box doesnt show up among the devices when the device is in recovery mode. As there is no zip file for direct linux installation that i can use with flash from usb option. and the reset button beneath the av port does nothing, ive tried to flash multiple ARMbian Img files using both rufus and etcher but the screen just goes black whenever i press and hold the reset button beneath the av port. there is no option to install twrp as neither adb nor fastboot can connect whenever the device is in recovery mode. what to do?
-
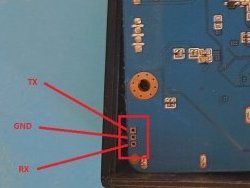
🏆 Become a sponsor, help to add other boards in armbian standart, you don't need to be a programmer to help the community, just need a copy of the ARM BOARD and a x86 computer to compile new versions. If you like what you see here and want to help: Donate Armbian the like button only costs a few dollars. Armbian Needs you help! Product Specification: Chipset: Rockchip RK3576 Octa Core ARM Mali G52 MC3 WIFI: WiFi6 11ax 1x1 80 MHz wifi controller: AP6275P RAM: DDR4 4GB/8GB ROM: eMMC 32GB/64GB/128GB OS: Android 14.0 || Armbian Vendor 6.1 Ethernet: 1000M Standard RJ-45 Bluetooth: BT 5.0 The RK3576 is indeed a lower-cost SoC but features four Cortex-A72 and four Cortex-A53 cores instead Android Base Files: H96-RK3576-ANDROID.dts H96-RK3576-ANDROID.dts H96-RK3576-BOX.dtb H96-RK3576-BOX.dtb RK3576_MiniLoaderAll.bin Vendor Kernel DTS: @RealAn H96-RK3576-VENDOR.dts Mainline status: Verify wifi controller: AP6275P Wifi Driver: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1n6x4tg5Xh24nWllOTJTq1ldVyDkK8W2Q/view?usp=sharing Flashing Tools: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1nLgPCBN0qmbzufWDFmISYc92JUpvwMPc/view?usp=sharing build_armbian.csc: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1VNR5QJlPylPsce9PI9O2TB3wOpshK2Bh/view?usp=sharing @hzdm Stock Firmware: method https://drive.google.com/file/d/1zLGvIxLE6vf8iSTjsyEr-Ly4MZ6ZahBB/view?usp=sharing Flashing Firmware Tutorial Factory Firmware for H96 Max M9 https://disk.yandex.ru/d/pWGEtRel0P9ejg https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1g63F8fGSLEA9iK2_Mqzd6F0xfaTRnGlm?usp=sharing Factory Firmware for H96 Max M9S https://disk.yandex.ru/d/H17eGTYCjgmCsg https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1Q360l5XbTVsWIvWkqy2xJ0sLpqHRSApM?usp=sharing TTL debug: RX TX GND pins: Enable SDCARD Reader: @rustamt method from 4pda Force board Maskrom Mode Maskrom Pins:
-
Can I enable wifi (SV6256P) in H616 DDR3 Tv box https://github.com/paolosabatino/ssv6x5x/tree/master or build from old kernel 4.4.x
-
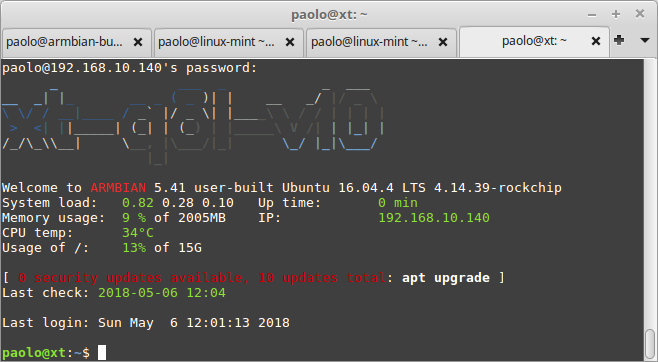
DISCLAIMER (PLEASE READ): everything you can find in this thread (binaries, texts, code snippets, etc...) are provided AS-IS and are not part of official Armbian project. For this reason not people from Armbian project nor myself are responsible for misuse or loss of functionality of hardware. Please don't ask about support or assistance in other non-community forums nor in the official Armbian github repository, instead post your questions in this thread, in the TV Boxes forum section (hardware related) or in the Peer-to-peer support section (general linux/software related). Thank you! This is CSC Armbian for XT-Q8L-V10 boards, also known as Chiptrip Q8, Vsmart Q8, ENY 3288 Q8, etc... All source code has been merged into Armbian mainline project. I still keep my personal public Armbian fork for experimental features: https://github.com/paolosabatino/armbian-build Nightly images: download directory Quick installation instructions on eMMC: Build or download your preferred Armbian image from Download directory and a copy of the Multitool; Burn the Multitool on an SD card; once done, place the Armbian image in images folder of the SD card NTFS partition; Plug the SD card in the TV box and plug in the power cord. After some seconds the blue led starts blinking and the Multitool appears; OPTIONAL: you can do a backup of the existing firmware with "Backup flash" menu option; Choose "Burn image to flash" from the menu, then select the destination device (usually mmcblk2) and the image to burn; Wait for the process to complete, then choose "Shutdown" from main menu; Unplug the sd card, then push the power button for 1 second (the led will turn blue) After 10 seconds HDMI will turn on and you will get logging messages; On first boot you will be asked for entering a password for root user of your choice and the name and password for a regular user Run armbian-config to configure timezone, locales and other personal options Congratulations, Armbian is now installed! Boot from SD Card/USB stick (with Armbian already installed in eMMC, empty eMMC or no eMMC😞 Build or download your preferred Armbian image from Download directory; Burn the image on your SD card/USB stick; Plug the SD card/USB stick in the device; Push the power button for 1 second (the led will turn blue); After 10 seconds HDMI will turn on and you will get logging messages; On first boot you will be asked for entering a password for root user of your choice and the name and password for a regular user Run armbian-config to configure timezone, locales and other personal options Congratulations, Armbian is now installed! Boot from SD Card/USB stick (with original firmware or other firmware): In case your box has the original firmware installed, use the Multitool to erase the internal flash. Don't worry, you will not brick your box: once the eMMC is emptied, the box will automatically boot from SD Card. This is called Maskrom mode and is common to all Rockchip devices. Instructions and download links for the Multitool are at the bottom of this post. After erasing the internal eMMC, just follow the "Boot from SD Card" procedure above and then you are fine. Boot priority: Newer images (those with mainline kernel >= 4.14.50) now support booting from multiple devices. Priority is fixed and boot devices are probed in this order: External SD card External USB storage device (Any USB Stick/Hard drive attached to USB host ports) Internal eMMC This way even if you install armbian to internal eMMC, you can still easily test different images booting from external devices. Experts notes: when armbian is installed into eMMC you get U-boot installed too in eMMC. This is important to know because the box won't boot in Maskrom Mode, but instead will always boot the embedded U-boot, no matter if you put an sdcard/usb stick. In practice the embedded U-boot is totally responsible for the boot priority. If you want to restore the Maskrom Mode, just erase U-boot from eMMC using this command: dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/mmcblk2 seek=64 count=8128 conv=sync,fsync Current status: Wireless: works. pretty fast and stable, signal is strong on my box; Bluetooth: works. I was able to transfer files and stream audio without problems USB ports: works, with autosuspend too. A quick benchmark show that transfer rate is quite good (topped at 34 MB/s) USB OTG: works in host mode. Transfer rate is very good (> 40 MB/s) MMC: works and is perfectly accessible as storage device. The images above with "eMMC friendly" have been tested and work when installed in eMMC using the standard armbian-config eMMC installer SDCard: works. legacy kernel is limited to high speed, while mainline works fine in UHS mode too. A quick benchmark with a Samsung EVO card shows the promised 48Mb/s read speed. Gigabit Ethernet: works, fast and reliably HDMI: works perfectly Serial: works Audio: both HDMI audio and SPDIF connector works IR remote: works on legacy and mainline kernels Reboot/Suspend process: rebooting the device is a working in progress, at the moment sometimes it works and sometimes it doesn't. Suspend is still not available. Hardware acceleration: everything which works for rk3288 boards applies here too. This guide or maybe the Media Testing Script will help you gain an hardware accelerated X11 and Chromium (using GL4ES I enjoyed Quake 2 from the start till the end, but also Quake and Quake III Arena work flawlessy, here a quick how-to to compile and install GL4ES) Multimedia: On mainline kernel 3D acceleration is provided by Panfrost driver and is already enabled. Hardware video decoding: https://forum.armbian.com/topic/19258-testing-hardware-video-decoding-rockchip-allwinner/ Multitool: The Multitool is a small but powerful tool to easy operate on internal eMMC flash of RK3288 devices. Features: Backup the content of internal eMMC Restore a previously backed-up image to eMMC Erase the eMMC (via fast blkdiscard or zero-fill as fallback) Burn an Armbian (or LibreELEC) image directly on the eMMC Provide a recovery shell for manual maintenance Windows-friendly: everything is placed in a NTFS partition Image compression format autodetection: they are decompressed on-the-fly during burn process Network support for remote maintenance via SSH (instructions to access via network here) Instructions are simple: Download the image from here Burn it on an sdcard Open the NTFS partition with your preferred file manager Place the images you want to burn on the device in images directory (backups will be stored in backups directory) Plug the sd card in the RK3288 device Power the device and wait few seconds, the Multitool menu will appear on screen and can be navigated with the keyboard Last edit: 07/06/2020 - updated installation instructions
-
Hello, sorry for my very bad english. I recently I bought a TV box with an h618 processor And I want to install Linux to make it a server but I only find images for the h616 processor, can I install one of these images on my TV box? It seems that the h616 processor and the h618 procesador are almost the same Thanks :D
-
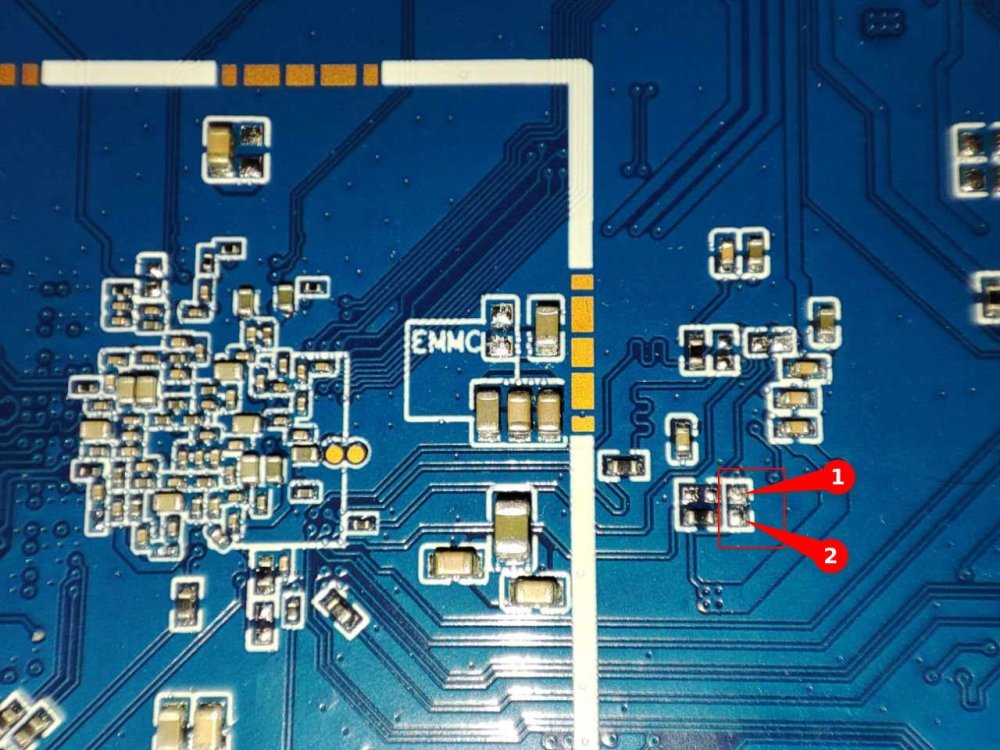
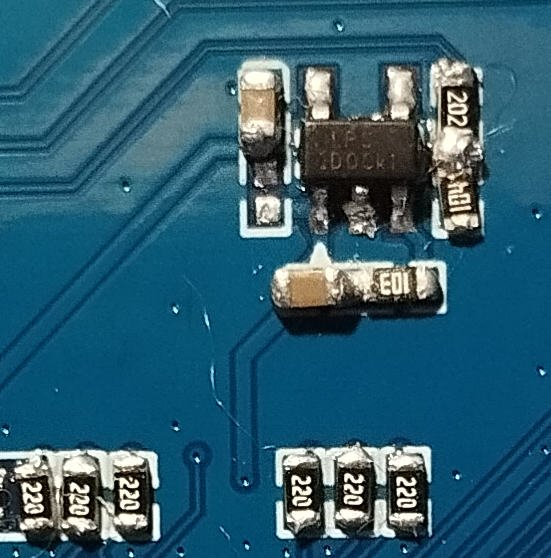
DISCLAIMERS (PLEASE READ): Everything you can find in this thread (binaries, texts, code snippets, etc...) are provided AS-IS and are not part of official Armbian project. For this reason not people from Armbian project nor myself are responsible for misuse or loss of functionality of hardware. THIS POST explains very well the troubles with TV Boxes and why they are not suitable for everyone Please don't ask about support or assistance in other non-community forums nor in the official Armbian github repository, instead post your questions in this thread, in the TV Boxes forum section (hardware related) or in the Peer-to-peer support section (general linux/software related). Following the recent thread on LibreElec forum about an unofficial image for rk3229 devices, I would like to make public the work made by me and @fabiobassa about bringing rk322x support to armbian. The project is now in -> mainline Armbian <- development fork -> here <- This first page and the last 3 or 4 pages of the thread are enough to get up to date with recent developments. Many useful experiences are scattered through the thread, but the most important things are collected here in the first page, so please read it carefully! Mainline kernel is fully supported and will receive most support in the future. Legacy kernel 4.4 is deprecated, but is kept around only for special purposes. What works: Should boot and work flawlessy on all boards with RK3228a, RK3228b and RK3229, with either DDR2 and DDR3 memories. Mainline u-boot Proprietary OPTEE provided as Trusted Execution Environment (needed for DRAM frequency scaling) All 4 cores are working Ethernet Serial UART (configured at 115200 bps, not 1.5Mbps!) Thermals, CPU and DRAM frequency scaling OTG USB 2.0 port (also as boot device!) EHCI/OHCI USB 2.0 ports MMC subsystem (including eMMC, SD and sdio devices) Hardware video acceleration NAND is available only on legacy kernel. To fully boot from NAND, use the Multitool and its steP-nand installation (instructions are below) Various WIFI over SDIO are supported (SSV6051P, SSV6256P, ESP8089, Realtek chips, etc...), ssv6256p driver is available only on legacy kernel Full GPU acceleration U-boot boot order priority: first the sdcard, then the USB OTG port and eventually the internal eMMC; you can install u-boot (and the whole system) in the internal eMMC and u-boot will always check for images on external sdcard/USB first. Unbrick: Technically, rockchip devices cannot be bricked. If the internal flash does not contain a bootable system, they will always boot from the sdcard. If, for a reason, the bootable system on the internal flash is corrupted or is unable to boot correctly, you can always force the maskrom mode shorting the eMMC clock pin on the PCB. Here there is the procedure, but you can also google around if you get stuck on a faulty bootloader, the technique is pretty simple and requires a simple screwdriver. There are however some unfortunate cases (expecially newer boards) where shorting the eMMC clock pin is difficult or impossibile, like eMMC or eMCP BGA chips with no exposed pins. In those cases pay double attention when burning something on the internal eMMC/eMCP and always test first the image from the sdcard to be sure it works before burning anything on eMMC/eMCP. Some useful links with pins, pads or procedures for some boards: Generic procedure for boards with non-BGA eMMC MXQPRO_V71 - eMCP H20 - eMCP ZQ01 - eMCP NAND vs eMMC vs eMCP difference: RK3228 and RK3229 tv boxes comes with three different flash memory chips: eMMC, NAND and eMCP. It does not depend upon the market name of the tv box and neither the internal board; manufacturers put whatever they find cheaper when they buy the components. NAND chip is just the non-volatile memory eMMC chip contains both the non-volatile memory plus a controller. eMCP chip contains the non-volatile memory, a controller for the non-volatile memory (like eMMC), but also contains a bank of DDR SDRAM memory on the same physical chip. The difference is very important, because eMMC and eMCP are far easier to support at various levels: the controller deals with the physical characteristics of the non-volatile memory, so the software has no to deal with. NAND chips instead are harder to support, because the software is required to deal with the physical characteristics and non-standard things that depends upon the NAND manufacturer. If you have a NAND chips you're unlucky because mainline kernel currently cannot access it, but also because you need special care and instructions explained later. You can discover if you have a NAND, eMMC or eMCP chip looking on the board are reading the signature on the flash memory chip. The Multitool (see later) also can detect which chip you have onboard: the program will warn you at startup if you have a NAND chip. NAND bootloader upgrade: IMPORTANT: don't do this is you have an eMMC or eMCP; skip this paragraph if you are unsure too! For very expert people who are having issues when (re)booting images, there is the chance to upgrade the bootloader on NAND. The NAND bootloader is nothing else than a regular idbloader (see official rockchip documentation) but contains some bits to correctly access the data on your flash memory. Upgrading requires to erase the existing flash content, in the worst case will require you to follow the Unbrick procedure above or restore an older but more compatible bootloader. If you are not mentally ready to overcome possible further issues, don't do this! The detailed instructions and the binaries are available at this post Multimedia: Mainline kernel: 3D acceleration is provided by Lima driver and is already enabled. Hardware video decoding: https://forum.armbian.com/topic/19258-testing-hardware-video-decoding-rockchip-allwinner/ Deprecated legacy kernel: multimedia features, like OpenGL/OpenGL ES acceleration, hardware accelerated Kodi, ffmpeg and mpv you can take a look to this post An effective tutorial from @Hai Nguyen on how to configure a box as a hi-quality music player using an USB audio card, and controlling it via remote control is available in this post Brief explanation about kernel naming: current kernel is the mainline LTS kernel version, most maintained and tested. This is the suggested version for production devices. If you don't know what to pick, pick this. legacy kernel (version 4.4) is provided by manufacturer; it is deprecated, unmaintained and not suggested. edge kernel is the development mainline kernel version, with experimental features and drivers; usually stable but perhaps suitable for production devices. You can switch from one kernel flavour to another using armbian-config or manually via apt. Installation (via SD card): Building: You can build your own image follow the common steps to build armbian for other tv boxes devices: when you are in the moment to choose the target board, switch to CSC/TVB/EOL boards and select "rk322x-box" from the list. Download prebuilt images from the following links: Archive builds (GPG-signed) - https://imola.armbian.com/dl/rk322x-box/archive/ SUGGESTED - Nightly built from trunk each week by Armbian servers (GPG-signed) - https://github.com/armbian/community Old images provided by me (unsigned and outdated) - https://users.armbian.com/jock/rk322x/armbian/stable Archived/older images: https://armbian.hosthatch.com/archive/rk322x-box/archive/ Multitool: The Multitool is a small but powerful tool to do quick backup/restore of internal flash, but also burn images and general system rescue and maintenance via terminal or SSH. Compressed images will be uncompressed on fly. Multitool - A small but powerful image for RK322x TV Box maintenance (instructions to access via network here) Quick installation instructions on eMMC: Build or download your preferred Armbian image and a copy of the Multitool; Burn the Multitool on an SD card; once done, place the Armbian image in images folder of the SD card NTFS partition; Plug the SD card in the TV box and plug in the power cord. After some seconds the blue led starts blinking and the Multitool appears; OPTIONAL: you can do a backup of the existing firmware with "Backup flash" menu option; Choose "Burn image to flash" from the menu, then select the destination device (usually mmcblk2) and the image to burn; Wait for the process to complete, then choose "Shutdown" from main menu; Unplug the power cord and the SD card, then replug the power cord; Wait for 10 seconds, then the led should start blinking and HDMI will turn on. The first time the boot process will take a couple of minutes or more because the filesystem is going to be resized, so be patient and wait for the login prompt. On first boot you will be asked for entering a password for root user of your choice and the name and password for a regular user Run sudo rk322x-config and select your board characteristics to enable leds, wifi chips, high-speed eMMC, etc... Run sudo armbian-config to configure timezone, locales and other personal options Congratulations, Armbian is now installed and configured! Despite the procedure above is simple and reliable, I always recommend to first test that your device boots Armbian images from SD Card. Due to the really large hardware variety, there is the rare chance that the images proposed here may not boot. If a bad image is burned in eMMC, the box may not boot anymore forcing you to follow the unbrick section at the top of this post. Quick installation instructions on NAND: Build or download your preferred Armbian image and a copy of the Multitool; Burn the Multitool on an SD card; once done, place the Armbian legacy kernel image in images folder of the SD card NTFS partition; Plug the SD card in the TV box and plug in the power cord. After some seconds the blue led starts blinking and the Multitool appears; OPTIONAL: you can do a backup of the existing firmware with "Backup flash" menu option; Choose "Burn Armbian image via steP-nand" from the menu, then select the destination device (usually rknand0) and the image to burn; Wait for the process to complete, then choose "Shutdown" from main menu; Unplug the power cord and the SD card, then replug the power cord; Wait for 10 seconds, then the led should start blinking and HDMI will turn on. The first time the boot process will take a couple of minutes or more because the filesystem is going to be resized, so be patient and wait for the login prompt. On first boot you will be asked for entering a password for root user of your choice and the name and password for a regular user Run sudo rk322x-config and select your board characteristics to enable leds, wifi chips, etc... Run armbian-config to configure timezone, locales and other personal options Congratulations, Armbian is now installed! Alternative: you can install the bootloader in NAND and let it boot from SD Card or USB: Download a copy of the Multitool and burn it on an SD card; Plug the SD card in the TV box and plug in the power cord. After some seconds the blue led starts blinking and the Multitool appears; RECOMMENDED: make a backup of the existing firmware with "Backup flash" menu option; Choose "Install Jump Start for Armbian" menu option: the Jump Start uses the internal NAND to boot from external SD Card or external USB Stick; Follow the general instructions to boot from SD Card below, skip the first erase eMMC step. Quick installation instructions to boot from SD Card: If you are already running Armbian from eMMC, skip to the next step. Instead if you are running the original firmware you need to first erase the internal eMMC; to do so download the Multitool, burn it on an SD Card, plug the SD Card and power the TV Box. Use "Backup flash" if you want to do a backup of the existing firmware, then choose "Erase flash" menu option. Build or download your preferred Armbian image; Uncompress and burn the Armbian image on the SD Card; Plug the SD Card in the TV Box and power it on; Wait for 10 seconds, then the led should start blinking and HDMI will turn on. The first time the boot process will take a couple of minutes or more because the filesystem is going to be resized, so be patient and wait for the login prompt; On first boot you will be asked for entering a password for root user of your choice and the name and password for a regular user Run sudo rk322x-config and select your board characteristics to enable leds, wifi chips, high-speed eMMC or NAND, etc... Run armbian-config to configure timezone, locales and other personal options, or also to transfer the SD Card installation to internal eMMC; Congratulations, Armbian is running from SD Card! A note about boot device order: With Armbian also comes mainline U-boot. If you install Armbian or just the bootloader in the eMMC or the Jump Start on internal NAND, the bootloader will look for valid bootable images in this order: External SD Card External USB Stick in OTG Port Internal eMMC Installation (without SD card, board with eMMC) If you have no sd card slot and your board has an eMMC, you can burn the armbian image directly on the internal eMMC using rkdeveloptool and a male-to-male USB cable: Download your preferred Armbian image from Armbian download page and decompress it. Download the rk322x bootloader: rk322x_loader_v1.10.238_256.bin Download a copy of rkdeveloptool: a compiled binary is available in the official rockchip-linux rkbin github repository. Unplug the power cord from the tv box Plug an end of an USB Male-to-male cable into the OTG port (normally it is the lone USB port on the same side of the Ethernet, HDMI, analog AV connectors) while pressing the reset microbutton with a toothpick. You can find the reset microbutton in a hole in the back of the box, but sometimes it is hidden into the AV analog jack Plug the other end of the USB Male-to-male cable into an USB port of your computer If everything went well, run lsusb: you should see a device with ID 2207:320b Run sudo rkdeveloptool rd 3 (if this fails don't worry and proceed to next step) Run sudo rkdeveloptool db rk322x_loader_v1.10.238_256.bin Run sudo rkdeveloptool wl 0x0 image.img (change image.img this with the real Armbian image filename) Unplug the power cord Done! Installation (without SD card, board with NAND) If you are in the unfortunate case you can't use an SD card for installation and your board has a NAND chip, you still have an option to use the quick Multitool installation steps via USB. Obtain a copy of rkdeveloptool: a compiled binary is available in the official rockchip-linux rkbin github repository. Unplug the power cord from the tv box Plug an end of an USB Male-to-male cable into the OTG port (normally it is the lone USB port on the same side of the Ethernet, HDMI, analog AV connectors) while pressing the reset microbutton with a toothpick. You can find the reset microbutton in a hole in the back of the box, but sometimes it is hidden into the AV analog jack Plug the other end of the USB Male-to-male cable into an USB port of your computer If everyting went well, using lsusb you should see a device with ID 2207:320b Run sudo rkdeveloptool wl 0x4000 u-boot-main.img (download u-boot-main.img.xz , don't forget to decompress it!) Unplug the power cord Now you can follow the instructions on how to install on eMMC/NAND via SD card, just use instead an USB stick to do all the operations and plug it into the USB OTG port. Once you reboot, USB OTG port will be used as a boot device. NOTE: NAND users without SD slot may be unhappy to know that it will be difficult to do extra maintenance with Multitool in case something breaks in the installed Armbian system: installing u-boot-main.img makes the installed system unbootable because it is missing the NAND driver. Alternative backup, restore and erase flash for EXPERTS: These backup, restore and erase flash procedures are for experts only. They are kept here mostly for reference, since the Multitool is perfectly able to do same from a very comfy interface and is the suggested way to do maintenance. Backup: Obtain a copy of rkdeveloptool: a compiled binary is available in the official rockchip-linux rkbin github repository. If you prefer, you can compile it yourself from the sources available at official rockchip repository Unplug the power cord from the tv box Plug an end of an USB Male-to-male cable into the OTG port (normally it is the lone USB port on the same side of the Ethernet, HDMI, analog AV connectors) while pressing the reset microbutton with a toothpick. You can find the reset microbutton in a hole in the back of the box, but sometimes it is hidden into the AV analog jack Plug the other end of the USB Male-to-male cable into an USB port of your computer If everyting went well, using lsusb you should see a device with ID 2207:320b change directory and move into rkbin/tools directory, run ./rkdeveloptool rfi then take note of the FLASH SIZE megabytes (my eMMC is 8Gb, rkdeveloptool reports 7393 megabytes) run ./rkdeveloptool rl 0x0 $((FLASH_SIZE * 2048)) backup.data (change FLASH_SIZE with the value you obtained the step before) once done, the internal eMMC is backed up to backup.data file Restore: first we have to restore the original bootloader, then restore the original firmware. Running rkdeveloptool with these switches will accomplish both the jobs: ./rkdeveloptool db rk322x_loader_v1.10.238_256.bin Downloading bootloader succeeded. ./rkdeveloptool ul rk322x_loader_v1.10.238_256.bin Upgrading loader succeeded. ./rkdeveloptool wl 0x0 backup.data Write LBA from file (100%) Download here: Erase the flash memory: clearing the internal eMMC/NAND memory makes the SoC look for external SD Card as first boot option. If there isn't any suitable SD Card, the SoC enters maskrom mode, which can then be used for full eMMC/NAND access using rkdeveloptool. This is perfectly fine if your box has an eMMC flash memory. NOTE: In case you have a NAND flash memory this option is however discouraged. The original bootloader contains some special parameters to correctly access the data. Clearing the flash memory will probably garbage the NAND data and restoring the bootloader may require some special instructions. Obtain a copy of rkdeveloptool: a compiled binary is available in the official rockchip-linux rkbin github repository. If you prefer, you can compile it yourself from the sources available at official rockchip repository Unplug the power cord from the board Plug an end of an USB Male-to-male cable into the OTG port (normally it is the lone USB port on the same side of the Ethernet, HDMI, analog AV connectors) while pressing the reset microbutton with a toothpick. You can find the reset microbutton in a hole in the back of the box, but sometimes it is hidden into the AV analog jack Plug the other end of the USB Male-to-male cable into an USB port of your computer If everyting went well, using lsusb you should see a device with ID 2207:320b run ./rkdeveloptool ef and wait a few seconds once done, the internal eMMC is erased and the device will boot from the sdcard from now on Partecipation and debugging: If you want to partecipate or need help debugging issues, do not hesitate to share your experience with the installation procedure of the boxes. In case of issues and missed support, provide as many as possible of these things is very useful to try and bring support for an unsupported board: some photos of both sides of the board. Details of the eMMC, DDR and Wifi chips are very useful! upload the device tree binary (dtb) of your device. We can understand a lot of things of the hardware from that small piece of data; and alternative is a link to the original firmware (you can do a full backup with the Multitool); dmesg and other logs (use armbianmonitor -u that automatically collects and uploads the logs online) attach a serial converter to the device and provide the output of the serial port; Critics, suggestions and contributions are welcome! Credits: @fabiobassa for his ideas, inspiration, great generosity in giving the boards for development and testing. The project of bringing rk322x into armbian would not have begun without his support! Justin Swartz, for his work and research to bring mainline linux on rk3229 (repository here) @knaerzche for his great contribution to libreelec support and mainline patches @Alex83 for his patience in testing the NAND bootloader upgrade procedure on his board @Jason Duhamell for his generous donation that allowed researching eMCP boards and esp8089 wifi chip
- 3075 replies
-
23
-
DISCLAIMER (PLEASE READ): everything you can find in this thread (binaries, texts, code snippets, etc...) are provided AS-IS and are not part of official Armbian project. For this reason not people from Armbian project nor myself are responsible for misuse or loss of functionality of hardware. Please don't ask about support or assistance in other non-community forums nor in the official Armbian github repository, instead post your questions in this thread, in the TV Boxes forum section (hardware related) or in the Peer-to-peer support section (general linux/software related). Thank you! This thread is to give stable and mature long-term range support to rk3318/rk3328 found in many tv boxes in Armbian project as Community Supported Configuration (CSC). The current work is mainlined into Armbian project, but your mileage may vary; most recent developments live on my personal fork on github -> here <- Important notes: is just a personal opinion, but apparently widely supported, that rk3318 chip is not an official rockchip part. They probably are scrap rk3328 parts which have not passed conformance tests but are sold anyway to tv boxes manufacturers. They don’t reach the same operating frequency of the rk3328, have much higher leakage currents (and thus higher temperatures) and often the boards they are installed on are low quality with low quality components, in fact a very very common issue is the eMMC failure due to bad parts and bad soldering. So said, I personally suggest not to buy any rk3318 tv box, but instead find a properly supported SBC (Single Board Computer) if you need a reliable product. In the unfortunate case you already have such product, this thread may help you have some fun with them. What works: • Works on RK3318 and RK3328 TV boxes with DDR3 memories • Mainline u-boot • Mainline ATF provided as Trusted Execution Environment • All 4 cores are working • Ethernet • Serial UART (configured at stock 1.5Mbps) • Thermals and frequency scaling • OTG USB 2.0 port (also as boot device!) • EHCI/OHCI USB 2.0 ports and XHCI USB 3.0 ports • MMC subsystem (including , SD and sdio devices) • Hardware video acceleration (fully supported via RKMPP on legacy kernel, support via hantro and rkvdec kernel driver on mainline) • Various WIFI over SDIO are supported • Full acceleration on legacy kernel and mainline kernel • U-boot boot order priority: first the sdcard, then the USB OTG port and eventually the internal ; you can install u-boot (and the whole system) in the internal and u-boot will always check for images on external sdcard/USB first. Unbrick: Technically, rockchip devices cannot be bricked. If the internal flash does not contain a bootable system, they will always boot from the sdcard. If, for a reason, the bootable system on the internal flash is corrupted or is unable to boot correctly, you can always force the maskrom mode shorting the clock pin on the PCB. The procedure is explained here for rk322x, but for rk3318/28 is the same. In most of the rk3318/28 boards, shorting the clock pin is difficult or impossible because eMMC are BGA chips with no exposed pins. Pay double attention when burning something on the internal flash memory and always test first the image booting from the sdcard to be sure it works before burning anything in internal flash. This is a list of posts where forum users have been able to spot the eMMC clock pin to trigger the maskrom mode: H96 Max+ (board signature: RK3318_V1.4) by @Gausus X88 PRO 10 (board signature: X88_PRO_B) by @mathgaming HK1 Max (board signature YX_RK3318) by @Constantin Gatej Ninkbox N1 Max RK3318 by @enigmasphinx Hongtop H50 (board signature t98-3318-221-v11) by @GmP Partecipation and debugging: If you want to partecipate or need help debugging issues, do not hesitate to share your experience with the installation procedure of the boxes. In case of issues and missed support, provide as many as possible of these things is very useful to try and bring support for an unsupported board: some photos of both sides of the board. Details of the eMMC, DDR and Wifi chips are very useful! upload the device tree binary (dtb) of your device. We can understand a lot of things of the hardware from that small piece of data; and alternative is a link to the original firmware (you can do a full backup with the Multitool); dmesg and other logs (use armbianmonitor -u that automatically collects and uploads the logs online) attach a serial converter to the device and provide the output of the serial port; Multimedia: Mainline kernel: 3D acceleration is provided by Lima driver and is already enabled. Hardware video decoding: https://forum.armbian.com/topic/19258-testing-hardware-video-decoding-rockchip-allwinner/ Legacy kernel: If you need multimedia features, like OpenGL/OpenGL ES acceleration, hardware accelerated Kodi, ffmpeg and mpv you can take a look to this post Installation (via SD card): Building: You can build your own image follow the common steps to build armbian for other tv boxes devices: when you are in the moment to choose the target board, switch to /TVB/ boards and select "rk3318-box" from the list. Prebuilt images: Nightly stables - built from trunk by Armbian servers and GPG-signed: https://github.com/armbian/community Multitool: Multitool - A small but powerful image for RK3318/RK3328 TV Box maintenance. Download it from here Quick installation instructions on eMMC: Build or download your preferred Armbian image and a copy of the Multitool; Burn the Multitool on an SD card; once done, place the Armbian image in images folder of the SD card NTFS partition; Plug the SD card in the TV box and plug in the power cord. After some seconds the blue led starts blinking and the Multitool appears; OPTIONAL: you can do a backup of the existing firmware with "Backup flash" menu option; Choose "Burn image to flash" from the menu, then select the destination device (usually mmcblk2) and the image to burn; Wait for the process to complete, then choose "Shutdown" from main menu; Unplug the power cord and the SD card, then replug the power cord; Wait for 10 seconds, then the led should start blinking and HDMI will turn on. The first time the boot process will take a couple of minutes or more because the filesystem is going to be resized, so be patient and wait for the login prompt. On first boot you will be asked for entering a password for root user of your choice and the name and password for a regular user Run rk3318-config to configure the board specific options Run armbian-config to configure timezone, locales and other personal options Congratulations, Armbian is now installed! Despite the procedure above is simple and reliable, I always recommend to first test that your device boots Armbian images from SD Card. Due to the really large hardware variety, there is the rare chance that the images proposed here may not boot. If a bad image is burned in , the box may not boot anymore forcing you to follow the unbrick section at the top of this post. Quick installation instructions to boot from SD Card: If you are already running Armbian from eMMC, skip to the next step. Instead if you are running the original firmware you need to first erase the internal flash; to do so download the Multitool, burn it on an SD Card, plug the SD Card and power the TV Box. Use "Backup flash" if you want to do a backup of the existing firmware, then choose "Erase flash" menu option. Build or download your preferred Armbian image; Uncompress and burn the Armbian image on the SD Card; Plug the SD Card in the TV Box and power it on; Wait for 10 seconds, then the led should start blinking and HDMI will turn on. The first time the boot process will take a couple of minutes or more because the filesystem is going to be resized, so be patient and wait for the login prompt; On first boot you will be asked for entering a password for root user of your choice and the name and password for a regular user Run rk3318-config to configure the board specific options Run armbian-config to configure timezone, locales and other personal options, or also to transfer the SD Card installation to internal ; Congratulations, Armbian is running from SD Card! Tutorial - How to install Armbian on your TV Box (by @awawa) : https://www.hyperhdr.eu/2022/01/tv-box-mania-i-part-x88-pro-10.html A note about boot device order: With Armbian also comes mainline U-boot. If you install Armbian, the bootloader will look for valid bootable images in this order: External SD Card External USB Stick in OTG Port Internal The Multitool does not boot / How to burn image directly on eMMC: Some boards have the sdcard attached to an auxiliary (called also sdmmc_ext or external) controller which is not the common one. Forum findings declare that those boards are not able to boot from sdcard with stock firmware and they neither do in maskrom mode: the stock firmware always boots even if you put the multitool on sdcard. In such case, burning images directly on eMMC is the only way to have a working Armbian installation. You can follow these instructions by @fabiobassa to burn images directly on eMMC: https://forum.armbian.com/topic/17597-csc-armbian-for-rk3318rk3328-tv-box-boards/?do=findComment&comment=130453 Notes and special hardware: Script to change DDR memory frequency here Wireless chip AP2734, SP2734, HY2734C and similars: they are clones of AmPAK AP6334 which is combo wifi + bluetooth of broadcom BCM4334/B0 chips. You may need a special nvram file, instructions by @paradigman are here Critics, suggestions and contributions are welcome! Credits: @fabiobassa for his ideas, inspiration, great generosity in giving the boards for development and testing. The project of bringing rk3318 into armbian would not have begun without his support! @hexdump for his precious support in early testing, ideas and suggestions @MX10.AC2Nfor his patience in testing mxq-rk3328-d4 board support All the rockhip64 maintainers at Armbian project who have done and do most of the work to support the platform
- 1971 replies
-
20
-
Currently working on a build for this device. It boots and is about 90% functional on 6.6 and 6.7 Kernel https://github.com/sicXnull/armbian-build/tree/X96Q-TVBOX-LPDDR3 Working - Desktop - Ethernet - Wifi Not working - DTS could use some work. Right now it does not detect internal EMMC so installing to EMMC is not an option. - Likely other things i've missed. I've uploaded two images to my git. Full w/Mate Desktop Minimal/Server Feel free to compile this yourself if you don't trust my images, it's encouraged. Changes are on the X96Q-TVBOX-LPDDR3 Branch Full W/Desktop ./compile.sh build BOARD=x96q-tvbox BRANCH=current BUILD_DESKTOP=yes BUILD_MINIMAL=no EXPERT=yes KERNEL_CONFIGURE=no KERNEL_GIT=shallow RELEASE=bookworm Minimal/Server ./compile.sh build BOARD=x96q-tvbox BRANCH=current BUILD_DESKTOP=no BUILD_MINIMAL=yes EXPERT=yes KERNEL_CONFIGURE=no KERNEL_GIT=shallow RELEASE=bookworm
-
I'm been trying to install Armbian on this TV.BOX console. I already test bookworm xfce image of Armbian as like the last XFCE image → Armbian_community_26.2.0-trunk.357_Aml-s9xx-box_noble_current_6.18.7_xfce_desktop I als test minimal images ad they don't work. The spces of console are : Processor (CPU)Amlogic S905X3 Quad-core ARM Cortex-A55, up to 1.91GHz Graphics (GPU)Mali-G31 MP2 RAM4GB DDR3 Storage (ROM)32GB eMMC Video OutputHDMI, supports up to 8K@24fps (Android system) and 1080p (EmuELEC system) Connectivity2.4G/5G Dual-band Wi-Fi, 10/1000M Ethernet LAN, Bluetooth 4.0 Ports1x USB 3.0, 4x USB 2.0, HDMI, Ethernet, DCIN (Power), TF card slot, AV output I test to boot the stock images just after download them and the boot shows the HK1Series and then goes to internal android system (tvbox) so failed. When I do the steps to put dtb file, edit extlinux.conf and rename properly u-bott to u-boot.ext (I search and test test many dtb files as like meson-sm1-hk1box-vontar-x3.dtb, meson-sm1-h96max-x3.dtb, sm1_s905x3_4g_1gbit.dtb, sm1_s905x3_4g.dtb as like others that I download on web when I search info about install armbian on s905x tv boxes). I also try to see if I can edit a .dts file and then convert to .dtb qhen I did It doesn't work. So none of steps above works. But I find one image system that works called devmfc that has only a minimal image similar to a server image only with tty text. https://github.com/devmfc/debian-on-amlogic/releases I inspect the .image of this system, and I find that if I copy the boot.scr, boot.script and cfgload to the /boot partiton of the armbian systems and boot the Sper Console it goes to a pink screen and then after a minute just reboot or goes to hkseries system. So I think if I can edit boot.scr, bootscript and cfgload maybe I can put the right data to force boot the real kernel of armbian. Maybe then armbian works. I use Linux and try to open those files with text editor but doesn't work. Anyone knows How I can edit this files ? Any user can boot armbian on this console TvBox ? Thanks.
-
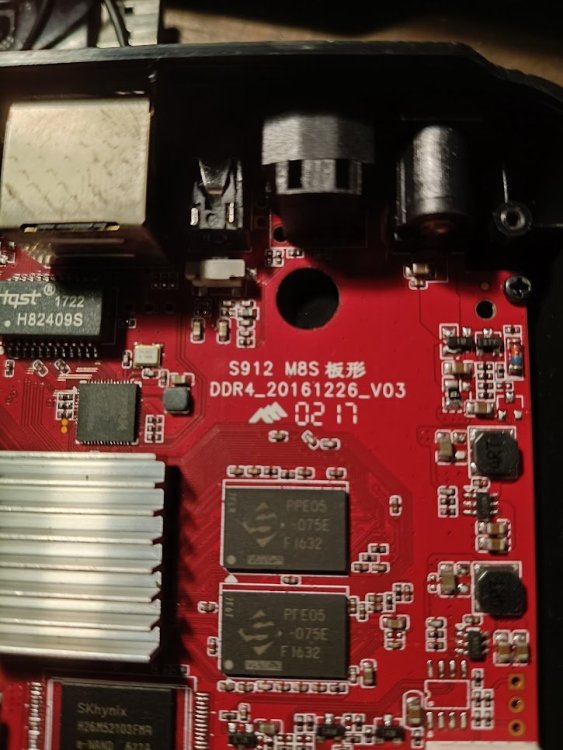
Hello, I have some troubles with this TVBOX: it runs armbian and other distros correctly, using the meson-gxm-t95z-plus.dtb but sometimes wifi goes into kernel panic at boot, and when it does, the whole system becomes unstable (i.e. not rebooting, eth0 hangs...). I have extracted the original .DTB from the only firmware that exists for this box, the ancient 6.0 Marshmellow Android (I guess it's a 3.x kernel...). I attach it to this message hoping someone more expert than me can help in making it work ina more stable manner. I attach a picture of the board also, it reads "M8S". Box has 2GB ram and 16GB eMMC, brcmfmac wifi/bt and ZTE PHY chip. meson1.dtb
-
Hi, I would like to know if its possible to boot from SD card in my model of Android TV BOX. It does not have a reset button but has an update app. Its a Giga TV Box HD890 4K. It has an Amlogic CPU I do all the process of installing Armbian in the SD card, Android starts an update and it says: "Map file is too short". I really dont know what I have to do to enable multi boot. Installation is aborted. Im getting really upset for not being able to install Armbian. Any help to this issue would be really welcome. Sorry for my bad english
-
Hi everybody, I just bought an X96 X6 TV box (8G/64G) to run Home Assistant. However it is not popular so there is no Armina for it. Home Assistant requires Debian 11/12 (linux kernel, no desktop version) to operate. Hope everyone can help me. Thank you very much. I only need 1 file *.img file to install Home Assistant, no need: USB, wifi, Bluetooth... because it can be difficult. Thank you very much!
-
Hello everybody. I'm new to this and I would like to install Linux on my BTV X p212 TV box. I saw that there are several versions of systems but I couldn't find them for this specific one and I would like to know if you can help me? Please. Ps: I searched here on the forum, google but I couldn't find it.
-

internal wifi "x96 max plus" tv box wifi chip "CDTech 47W3155"
SteeMan replied to Jain Ziad's topic in Amlogic CPU Boxes
Moved to amlogic TV ox forum -

Concerns before trying to boot Armbian from SD card on GS King-X
marfalk replied to marfalk's topic in Amlogic CPU Boxes
Thank you. I have managed to successfully boot Armbian from SD card. Android is preserved. Now I am trying to install (move) Armbian (the "/root" partition) to an external USB drive. I run "armbian-config", then I pick "System" --> "Storage", but no "Install" (Copy the running Armbian system to another device) option is listied (according to the documentation here). I get only the following items: Download a fresh, official Armbian OS image and write it to a device Enable read only filesystem Enable Network filesystem (NFS) support etc... I have tried also in Terminal: "armbian-config --cmd STO001" but I get an error. In the instructions for TV boxes here it says: "running the shell script in the /root directory: install-aml.sh" But it refers to installing (moving) Armbian to the internal eMMC, if I am not mistaken. Is it possible to install it either to an external USB HDD or internal SATA HDD? -
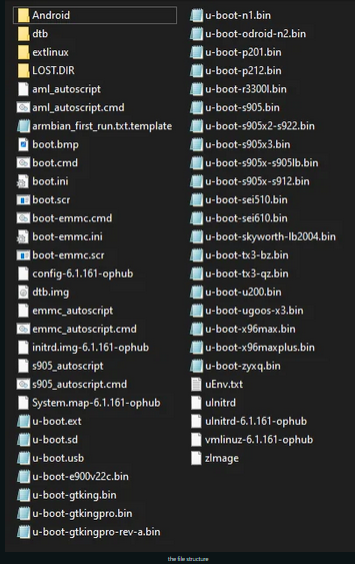
These instructions are for Amlogic CPUs for TV Boxes. Note: If you have previously run other distributions on the box such as coreelec the below installation will not work. You will need to restore the original android firmware before attempting the install. coreelec changes the boot environment in ways that are incompatible with these Armbian builds. Download links: Weekly Community Rolling Builds: https://www.armbian.com/amlogic-s9xx-tv-box/ or build your own image using the Armbian build framework Once you download your chosen build, you need to burn the image to an SD card. Generally balenaEtcher is recommended as it does a verification of the burn. Also be sure to use high quality SD cards. Once you have the SD card with your chosen build, then you need to edit the boot configuration file on the SD card. In the BOOT partition of the SD card there will be a file /boot/extlinux/extlinux.conf, that you need to edit. There will also be a extlinux.conf.template file to use as a reference. You will need to add a line into the extlinux.conf file for the Device Tree (dtb) file you will be using for your box. Place this line before the APPEND line as shown in the .template file. Basically you need to have the correct dtb for your box. You may need to attempt to use different dtb files until you find the one that works the best for your box's hardware (there are a bunch of dtb files in /boot/dtb/amlogic/... to try depending on your cpu architecture and hardware). It is unlikely that there will be a matching dtb file for your TV box. The idea is to find the one that works best for your box. This may mean that you try booting with different dtb files until you fine one that works good enough for your needs. By searching the forums you will find information about what dtbs other users have found work best for different boxes. Because you are booting from an SD card, you can easily try different dtb files. The dtd files are named by cpu family. So for example dtb files for the s905x2 cpu are named meson-g12a-*. Below there is a table that shows the identifiers for each familiy (g12a for s905x2 in this case). Next you need to copy the correct uboot for your box. This is needed for how these builds boot on amlogic boxes. There are four different u-boot files located in the /boot directory: u-boot-s905, u-boot-s905x-s912, u-boot-s905x2-s922, u-boot-s905x3 You need to copy (note copy not move) the u-boot file that matches your cpu to a new file named u-boot.ext in the /boot directory So for example with a TX3 mini box that has an s905w cpu you would copy u-boot-s905x-s912 to u-boot.ext: cp u-boot-s905x-s912 u-boot.ext (See table below for more details on which u-boot to use for which cpu) Once you have your SD card prepared you need to enable multiboot on the box. There are different ways documented to do this, but the most common is the "toothpick" method. The "toothpick" method means to hold the reset button while applying power to the box. The reset button is often hidden and located at the back of the audio/video jack connector. By pressing that button with a toothpick or other such pointed device you can enable multiboot. What you need to do is have the box unplugged, have your prepared sd card inserted, then press and hold the button while inserting the power connector. Then after a bit of time you can release the button. (I don't know exactly how long you need to hold the button after power is applied, but if it doesn't work the first time try again holding for longer or shorter times). You should now be booting into armbian/linux. Note that the first boot takes longer as it is enlarging the root filesystem to utilize the entire SD card. After you are satisfied that your box is working correctly for your needs you can optionally copy the installation from the SD card to internal emmc storage (assuming your box has emmc). (Note: Installing to emmc has some risks of bricking your box. Don't do this unless you feel you understand how to reinstall your box's android firmware) You install armbian to emmc by running the shell script in the /root directory: install-aml.sh. Note: It is not possible to install into emmc on boxes with the s905 cpu (s905x, s905w, s905x2, etc however should all be supported). It is recommended that you make a backup of emmc first. Also be prepared if anything goes horribly wrong with your emmc install to reinstall the android firmware using the Amlogic USB Burning Tool to unbrick your device. If you have or can find an original android firmware on the internet and you can generally (but not always) recover a bricked box using the Amlogic tool and the original firmware file. Mapping from CPU to uboot and dtb: u-boot-s905 s905 - gxbb u-boot-s905x2-s912 S905X - gxl S905W - gxl S905D - gxl S905L - gxl S805X - gxl S912 - gxm A311D - gxm u-boot-s905x2-s922 S905X2 - g12a S922 - g12b u-boot-s905x3 S905X3 - sm1 Not supported or not tested S805 - S905W2 - S905X4 - S805X2 - s4 A113D - axg A113X - axg Note: Followup posts in this thread should be limited to comments to improve or better understand these instructions. Other issues should be posted as new questions in the Amlogic CPU Boxes sub-forum.
- 38 replies
-
12