All Activity
- Past hour
-
Just to confirm this is a regression issue could you also test with a clean image rather than an upgrade? It is possible something could have gone wrong during the upgrade. If I understand correctly you are only using an SD card for booting, and the kernel and main OS reside on the SSD. have you preformed an integrity check of the USB, just to ensure there is no possible file corruption? Could you also please provide the output of mocp --debug? Best of luck Ryzer
- Today
-
T95Z Plus (Second one) running great
Tomas Catone replied to Tomas Catone's topic in TV Boxes running Armbian
Good to meet a fellow armbian android tv box fan. We need a logo or shorthand alias for fans 🤣. ZFS - was easy but not clear. Inside armbian-config under System/Storage is a script to install ZFS support. I did this and it didn't work... then undid it and then installed it a second time and it worked. Somewhere in there I also ran the standard commands for install: sudo apt install zfsutils-linux sudo apt install zfs-fuse Probably after the first uninstall... but the commands indicate failure. But then installing the second time seemed to work. Did that on both of these boxes I have working. Thanks for the ethtool command. Here's my results on box1 ports auto-negotiation: Yes Supported FEC modes: Not reported Advertised link modes: 10baseT/Half 10baseT/Full 100baseT/Half 100baseT/Full 1000baseT/Full Advertised pause frame use: Symmetric Receive-only Advertised auto-negotiation: Yes Advertised FEC modes: Not reported Link partner advertised link modes: 10baseT/Half 10baseT/Full 100baseT/Half 100baseT/Full 1000baseT/Full Link partner advertised pause frame use: Symmetric Receive-only Link partner advertised auto-negotiation: Yes Link partner advertised FEC modes: Not reported Speed: 1000Mb/s Duplex: Full Auto-negotiation: on master-slave cfg: preferred slave master-slave status: slave Port: Twisted Pair PHYAD: 0 Transceiver: external MDI-X: Unknown netlink error: Operation not permitted Current message level: 0x0000003f (63) drv probe link timer ifdown ifup Link detected: yes Not an expert and first time reading this command but looks like 1000 is the answer. Crazy thing - box 2 does not have the line "MDI-X: Unknown" shown towards the bottom and "Port: MII" instead of "Port: twisted pair" but is otherwise identical. Posting in case it helps anyone else - but these are beyond me. If you confirm that the above = 1000 I will update both my box running posts. By the way - Another favorite is Software/Management/Cockpit. Easy to see how the server is doing. Plus it has a built in terminal and file manager. Add that to Tailscale and you can check on the server or grab a file while out of the house. curl -fsSL https://tailscale.com/install.sh | sh Those are my favorites. What are yours? -
The way I understand it is that you only need the full firmware package in a few exceptional circumstances. What is the wifi chipset on your SBC? Do you have the wireless-regdb package installed? "dpkg -l wireless-regdb"
-
Thank you for sharing. Would be good to have your findings corroborated by some of official documentation. Thanks again for sharing.
-

Rolling Release and Kernel update concern
laibsch replied to Tomas Catone's topic in Amlogic CPU Boxes
If they boot, I wouldn't worry about any difference. -

Remote backup of SD card for an Orange Pi?
eselarm replied to Geoffrey Schaller's topic in Beginners
I know, but who cares if it is impractical IMO and various distros by default use that path. And RPiOS needs /boot/firmware, I myself use also /boot/uboot so I am more flexible w.r.t bootloaders. What is on boot FAT or in SPI-flash or tftpboot or else is secondary, the master (from package manager) is in rootfs. Read back my 1st message; there is option -p A snapshot is identified by its UUID, whether local or remote/other/foreign filesystem. So my backup tool/script figures that out. If an SD-card would be end of life or damaged scrub will notice it and then I regenerate the whole thing on a new SD-card from the latest transferred snapshot. I do not use /home for any meaningful data. All is on NAS. Some have no local storage except SPI for bootloader. I also treat all Linux computers the same, except those that are NAS or a clone of it. For rare Windows I indeed use 'imaging' although there is WinBTRFS. -
sounds good. good luck and keep us posted!
-
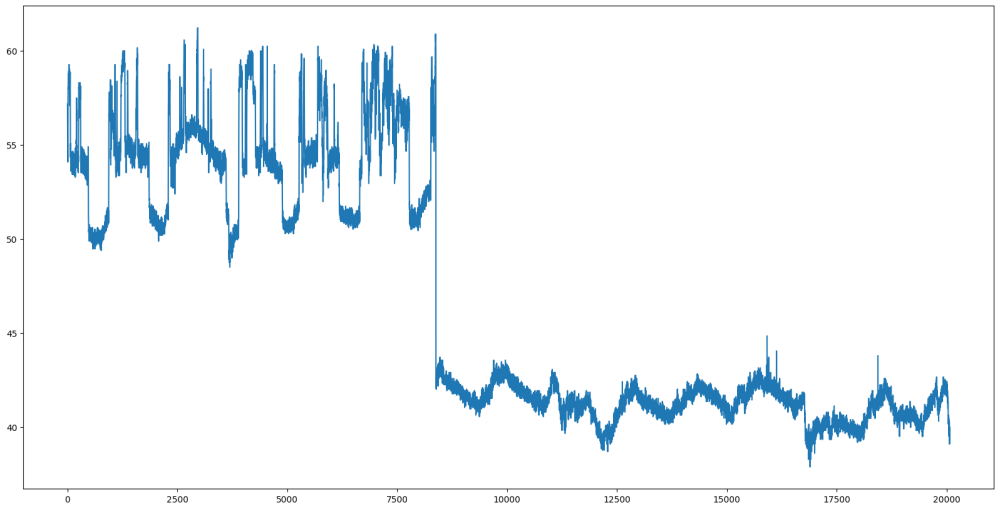
this is somewhat 'off-topic' but still relevant to 'orange pi zero 3' If Orange Pi Zero 3 is operated in warm climates (e.g. room temperature 30 deg C etc) , it can at times run up to like 60 deg C. this is in open still air adding a fan blowing at it reduce that by some 20 deg C to 40 deg C ! And this is my ghetto fan setup, no fancy case, no heatsink nothing, just a single long machine screw that lifts it up checking temperatures is easy > armbianmonitor -m Stop monitoring using [ctrl]-[c] Time CPU load %cpu %sys %usr %nice %io %irq Tcpu C.St. 18:03:39 480 MHz 0.00 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% 40.8 °C 0/7^C strictly speaking, 60 deg C is 'nothing to scream about' , I've a Rpi 4 hitting up 80 deg C and it throttles. similarly use a fan blowing at it + a heat sink over the cpu, drastically reduce running temperatures. for 'occasional' use, I don't think it is necessary to have a fan blowing at the Orange Pi Zero 3. I think it is feasible to run at lower temperatures if I disable and unclock the GPU and HDMI, but for now I'm not sure how to go about doing that. Initially, I'm thinking maybe the wifi is causing it, but now I don't think so, it is moderately likely the gpu is heating it up a bit. And still air don't seem to dissipate heat very well.
-
Thanks for the feedback, If that was the intention. If you try the version on the testing branch, that won't be an issue because 'btrfs du' (it is just slow and unnecessary) is no longer used. xD There are actually more changes coming to btrfs in the next release. Even looking into conversion from ext4 to btrfs. Oddly enough, I can backup my arch system with boot mounted at /boot/efi using the script on main branch, wonder why yours doesn't, so clearly distro DOES matter. But it soon won't matter for the problem you had, because it will be changed anyway. Besides, shrink-backup is not really intended to be used on a desktop computer, it's for sbc:s that usually are way less convoluted than a desktop setup. For ext4 and f2fs shrink-backup only covers root and boot partitions (if boot partition exists), btrfs is an exception where the script looks up existing subvolumes and creates them. As of now, the script also assumes all subvolumes starting with @ is a top volume, witch does not actually have to be the case, but changes are coming. Interesting to see you use /boot/efi (discouraged by linux kernel standards), and not /boot as boot partition, wonder why? I do the same, because I use timeshift that is built upon snapper. Timeshift also creates entries directly on my grub menu letting me boot into the ro snapshots and restore from there if needed. For others reading this: This is because if you roll back a snapshot where you have changed things in boot process and files inside /boot, you kinda want files inside /boot to be rolled back too or your system won't boot, hence letting /boot be part of the root subvolume and mount boot partition on /boot/efi instead. My point was, that the problem you mentioned, the database might become corrupted is not solved by using snapshots and btrfs, a database has to be closed and locked to be 100% sure it won't become corrupted in ANY copy process. (beside the fact that the database in the case of pihole is only a log and has nothing to do with the integrity of the application itself) I completely disagree with that. If I revert a snapshot because I messed something up on my system or something went wrong in an update for example, witch happens once in a while, I do NOT want my home to be over-written by an old snapshot. I also want to be able to read old log-files to figure out WHAT went wrong, so /home & /var/log in separate snapshots is absolutely a good thing for me. On a sbc I might agree that separate snapshots is a bit overkill though, but not in any way a bad idea. But if you actually use snapshots as a restore points on an sbc I argue /var/log is a good thing to have on separate snapshot. A snapshot takes no time at all, 1s I would guess, but what about the send|receive? Because a snapshot is completely worthless if the filesystem you took the snapshot from becomes corrupt, COW (copy on write) means you use the exact same data. That is why it's (or should be) general knowledge that a snapshot is NOT A BACKUP, but it becomes a file-backup if you send|receive it to a completely different filesystem. So the interesting part here is the send|receive because op asked about backups, and that takes about as long as a dd would take, while rsync probably does the file transfer in about 10% of that time. Also, again, shrink-backup takes everything, including boot process parts and makes an img file at small size (for two reasons, saving space and ability to use the img file on smaller storage device, moving from a 64GiB to a 32GiB sd-card for example) that can be written directly instead of also having to do a bunch of pretty complicated restore processes. And quite a few armbian images utilizes u-boot without a boot partition with header data written to the disk before root partition, shrink-backup covers that as-well. Generally, I treat snapshots as they are intended, as snapshots that can be used as RESTORE POINTS, and I use a backup application to make regular BACKUPS. On my desktop computer I use clonezilla that I have added a menu for in grub to easily boot into (you can make custom menus and boot directly into img/iso files in grub), and on all my sbc:s I obviously use shrink-backup. (for those who don't know, I am the maintainer of shrink-backup) I also have 260 "individual" incremental file backups of my home (and some other locations like /etc and my "file disk"), one every 6h using urbackup running on a rpi4 with a 6TB disk connected to it. It utilizes btrfs so the "individual" means they are just snapshots and only changed files actually take up more space. Lastly, if you don't actually utilize the functionality of running a system with multiple subvolumes, you don't even need to have a subvolume for /, you can just write files directly to the btrfs filesystem.
-
apparently new images for OrangePi Zero 3 Debian minimal IOT are out on github and the boards page thanks to @Igor, @TRay, et.al. https://www.armbian.com/orange-pi-zero-3/ https://github.com/armbian/community/releases/tag/25.8.0-trunk.309 ^ apparently a big release many images ( e.g. different variants and boards) are updated, but I checked only OrangePi Zero 3 Debian minimal IOT the feature for OrangePi Zero 3 according to recent build release https://github.com/armbian/build/releases/tag/v25.8.0-trunk.293 is https://github.com/armbian/build/pull/8334 the use of u-boot tag:v2025.04 likely improves boot time ddr ram size detection.
-

Desktop not showing Armbian 25.5.1 Noble Gnome, Orange Pi 5
Efe Çetin replied to compent's topic in Orange Pi 5
The image from https://dl.armbian.com/orangepi5/Noble_vendor_gnome works well for me. It might be good to see some GDM logs as i am not sure where the problem arises from. -
Yes, I know how to compile images. I'm still learning how to use git efficiently, though. Git bisect, I had never heard of before; but from what I read, is seems to be the right tool to find the breaking commit. But before I start into this possibly lengthy process, I came up with one theory, that I intend to check first: The initial assumption was, that the error is due to an API incompatibility in the Arm Trusted Firmware. My first intention was, to check if a newer version of the ATF was available, I just didn't know for wich part exactly I should look. Now I found out, that the working Image starts the "BL31"-thing right at the point where the current images fail: So, the first thing for me to check will be which version of "BL31" is used for the current images and if a newer version would be available and could be used instead. Unfortunately, i might not be able to work on this until next week. But I will report back as soon as there is new information.,
-

Remote backup of SD card for an Orange Pi?
eselarm replied to Geoffrey Schaller's topic in Beginners
I just mention the very basic, Btrfs has way to many features and options to make a generic image creating script. I see already 2 issues in the shrink-backup scrip, simple test: root@rock5b:~ # btrfs filesystem du -s --raw / Total Exclusive Set shared Filename ERROR: not a btrfs filesystem: /boot/efi WARNING: cannot access 'efi': Invalid argument WARNING: cannot access 'boot': Invalid argument ERROR: cannot check space of '/': Invalid argument This is on Opensuse Tumbleweed, but distro should not matter as I have a custom simple subvolume scheme. It is after 10+ years that I have a fully automated methods that just backup the structure I use in every Linux system so that it also can be 'played back' to a (sparse) image file or just raw device. I don't do any resizing, that is not essential to backup; I just re-create that same partition table (also backed up) so I have the same machine after a failed SD-card or HDD with too many bad sectors or just a clone template for a extra new SBC. I use a tool called snapper to create snapshots, both automatic and ad-hoc. It is also integrated in apt and zypper. So before the upgrade to pihole v6, a (read-only) snapshot is created. Also I was bothered by buggy v6, so I just take a read-write snapshot of the last know good/running read-only snapshot and set that that to default, then reboot, or even sync and power cycle. Of course that snapshot (UUID) is also as a differential created tree/folder on my NAS (in case the SD-card or so would fail). Long time ago installers created a lot of subvolumes, like for /home /var/log and many more. That indeed gets into big problems. Just use 1 for the root and snapshot that. That works fine for a workstation like machine with no real data stored locally (all is on NAS). Note that since kernel 6.1, btrfs send can send compressed data, so as it is stored on storage device. That saves time (and money) on mobile links for example. You can compress and decompress via rsync or ssh or vpn, but it costs extra battery energy. Also how long does "make atomic snapshots" take on a 4TB HDD of a subvolume of 2TB you think? -

NanoPi neo AIR no avalible COM port when connect to PC after update
Dandaman46 replied to Aknot's topic in Beginners
Hello @Aknot, better late than never? This is likely because USB OTG support is on out of the box now. You used to have to add an overlay to get it to work. You will need to modify the the overylays to change this. -
I found my NanoPi Neo Air's could not list or connect to some wifi networks. Some investigating found this was because channel 12/13 are disabled by default. Nothing in runtime had any effect on the output of iw reg get as it should have. Patching in some firmware fixes worked for me. wget http://ftp.be.debian.org/pub/software/network/wireless-regdb/wireless-regdb-2025.02.20.tar.xz tar xf wireless-regdb-2025.02.20.tar.xz sudo cp wireless-regdb-2025.02.20/regulatory.db /lib/firmware/ sudo cp wireless-regdb-2025.02.20/regulatory.db.p7s /lib/firmware/ sudo iw reg set AU #Australia I can now connect to wifi channel 13. Now for my question: I read in this old thread that armbian-firmware-full is required for wifi. would that mean that the full firmware package is desirable for the Nanopi Neo Air? When running apt-get install armbian-firmware-full it states it will consume an additional 1gb of disk space. Hardly desirable for a little device. VERSION v25.5.1 for NanoPi Air running Armbian Linux 6.12.30-current-sunxi
-
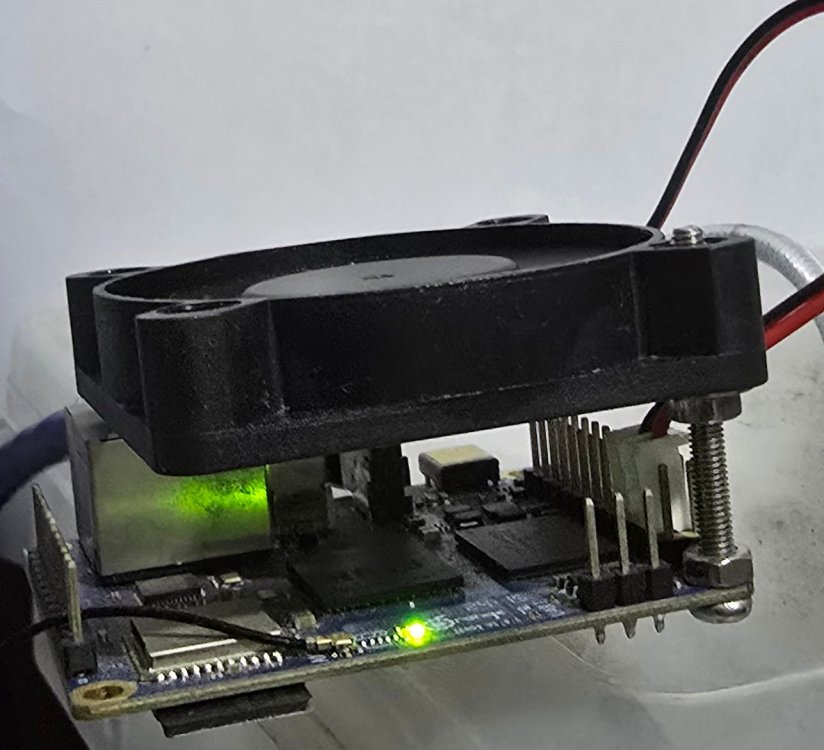
I disassembled my tv box - there are 4 screws under the 4 rubbery feet. Removed the motherboard and I drilled some holes of 1/4 inch (7 mm) diameter through the bottom plastic piece. Then I placed a USB fan underneath the tv box and wow the temperature really goes down and stays down around 45 C to 60 C depending on work load. The fans are 80mm and 120mm in size. I chose 120mm to be sure.
- Yesterday
-
That's a very good idea, especially if my online accounts that have my photos would ever become problematic for any reason. I have armbian on a tv box with SMB (samba) and with a USB 3.0 hard drive. The tv box is connected by gigabit ethernet to my home network. So I am going to try these apps - PhotoSync, FolderSync, CX File Explorer - on my android phone to backup my personal photos and videos and determine which is easiest and fastest. Which app on your phone/tablet have you chosen to use to backup your photos/videos?
-

T95Z Plus (Second one) running great
Pita Bread replied to Tomas Catone's topic in TV Boxes running Armbian
you can install "ethtool" and run ethtool eth0 on the command line. look for the line that shows " Speed: " how did you install ZFS in Armbian? -

Building Armbian Distribution with Kernel 6.10 for Orange Pi 5 Pro
C127 replied to Sergey Dulimov's topic in Rockchip
Hello everyone. @salas I have just implemented the out-of-box (OOB) network driver functionality in a new commit to the repository. This should serve as a temporary patch for now (or potentially a permanent one, depending on if/when the driver gets mainlined into the Linux kernel). @whywontitwork Thank you very much for the feedback and for testing the image. I need a bit more information to help track down the issue. My suspicion is that the system is successfully loading u-boot but failing to load the kernel. However, without debug logs, it's difficult to know the real cause. To help diagnose this, could you please tell me how you flashed the image? I flash my builds to a microSD card using the Balena Etcher software. Are you using the same method or a different one? I appreciate your support in getting the Orange Pi 5 Pro maintained! One of my main motivations for starting this project was to get Panthor support for the Mali GPU too. I can confirm that on my end, with the image I've built, the latest version of the drivers works correctly. Getting Vulkan and OpenGL running on an RK3588 board! -

Armbian for an old Allwinner A10 tablet
thewiseguyshivam replied to thewiseguyshivam's topic in Allwinner sunxi
The display does not work at all, just the backlight turns on and nothing shows up on the screen. I think looking at what you suggested I should try to take the good parts of these dts files and see what I can get working. After that I will try to compile uboot with that mixed dts file. I will take some time out to make this mixed dts file. I did try running pi-hole on this and it worked for some time, but it needs further testing. Will try the above and report back. Thanks, Shivam -

Desktop not showing Armbian 25.5.1 Noble Gnome, Orange Pi 5
compent replied to compent's topic in Orange Pi 5
Lightdm wasn't seen as being installed but I installed it just to see what happened but no change. sudo nano /home/*/.xsession-errors gave the following information. Xsession: X session started for test at Fri 20 Jun 07:04:16 BST 2025 dbus-update-activation-environment: setting DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS=unix:path=> dbus-update-activation-environment: setting DISPLAY=:10.0 localuser:test being added to access control list dbus-update-activation-environment: setting QT_ACCESSIBILITY=1 dbus-update-activation-environment: setting USER=test dbus-update-activation-environment: setting LANGUAGE=en_GB.UTF-8 dbus-update-activation-environment: setting XDG_SESSION_TYPE=x11 dbus-update-activation-environment: setting HOME=/home/test dbus-update-activation-environment: setting XRDP_PULSE_SINK_SOCKET=xrdp_chansrv> dbus-update-activation-environment: setting XRDP_PULSE_SOURCE_SOCKET=xrdp_chans> dbus-update-activation-environment: setting DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS=unix:path=> dbus-update-activation-environment: setting PULSE_SCRIPT=/etc/xrdp/pulse/defaul> dbus-update-activation-environment: setting LOGNAME=test dbus-update-activation-environment: setting XDG_SESSION_CLASS=user dbus-update-activation-environment: setting PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin> dbus-update-activation-environment: setting XRDP_SOCKET_PATH=/run/xrdp/sockdir dbus-update-activation-environment: setting XDG_RUNTIME_DIR=/run/user/1000 dbus-update-activation-environment: setting DISPLAY=:10.0 dbus-update-activation-environment: setting LANG=en_GB.UTF-8 I flashed an older image and this latest one (that had been working fine for a few weeks) and both ran fine from Micro SD cards or USB. I'm not sure what connection Efe Çetin has as it's an Orange Pi 5 board, so perhaps they have some form of official input to design. I'd love to know what triggered the change. And yes, like many things, no guarantees but if what happens can give pointers to preventing it happening to others in the future or recording potential solutions for those that might end up in the same position. -
I have long struggled with a problem with my Rock S0: If using the USB OTG port in device mode, the connection would suddenly drop randomly, minutes or sometimes hours after initialization. I spent months on and off looking for solutions, and I finally found one, so here it is if you ever find yourself having the same problem. Basically, it is caused by the SoC being very sensitive to voltage drops before the USB controller interprets it as the connection being lost. It's far more sensitive than it needs to be, given that my device is bus-powered and so the OS never actually needs to worry about a connection loss. If the connection is lost it is because I have unplugged the cable and so the device would be shut off regardless. Anyway, the solution lies deep within the RK3308's control registers, where I found the following: Three bits named "B_validsession reference tuning". There's no other explanation on what these bits does in the manual, but it sounded vaguely promising since I had been able to establish that "b-session valid" is actually the name of the status/interrupt that the vbus voltage affects in OTG device mode. Other registers related to the b-session valid status didn't work, however, including filter times, interrupt masks, force high bits, etc. But luckily this one register finally did the trick. The default value of these three bits are 000. Without any documentation I basically just had to guess what to do, so I tried setting them to 111 instead. And that seemed to work. It significantly lowered the voltage on the vbus pin required to trigger a disconnect signal. My connection was finally stable. Here's how you can do it yourself. First install memtool via apt, then run: memtool mw 0xFF008018 0x1C001C00
-
I have a pihole on one of my devices that I backup using shrink-backup. When pihole released 6.0 there was a bug that rendered my system unstable so I found it easier to revert back to 5.x until they fixed the bug. The restore worked without any issues whatsoever. The pihole database is only a db file and the records between the backup and to date is obv lost, but as for integrity of the system it's only a query log so it has no impact on pihole itself. As a matter of fact, you can run pihole without any db history at all. And IIRC the database history is 90 days by default, not one year. A btrfs send|recieve is only a file backup, it will never handle boot process or anything like that. You will also need to do it on every subvolume individually since send|recieve only takes one subvol, not even nested volumes. You will also have to make the source subvolume read only before issuing the send, but I guess that is what you mean by saying "make atomic snapshots". It's also very slow compared to rsync. Besides, using btrfs send|recieve does not solve the issue that copying a database that is in use might corrupt it, shutting down the application using the database before making a backup is. As a matter of fact, it might just make things even more complicated since you have to make the database (subvolume) read only during the send so the application might freak out from not being able to write to the database (unless you snapshot it first like you mention, but then you still have the same problem that an open database might break after being backed up). btrbk solves this (I think) by creating a snapshot (snapshots become read only by default) from the subvolume first and then send that, but you can't btrfs send|recieve a read/write subvolume, but again, does not solve the issue that the database is open. https://btrfs.readthedocs.io/en/latest/btrfs-send.html Fun fact: shrink-backup can backup btrfs devices. https://github.com/UnconnectedBedna/shrink-backup?tab=readme-ov-file#btrfs
-
Well its equivalent so other than vendor not beeing in a database does not count as custom in my books, but that is beside the point. Armbian correctly recognizes the size and I can write to it and that is important. Now flashing an existing image is simple. My preferred way is dd as described by Piter75: dd if=uboot.img of=/dev/mtdblock0 bs=4K for u-boot images and dd if=idbloader.img of=/dev/mtdblock0 seek=64 bs=512 conv=sync dd if=u-boot.itb of=/dev/mtdblock0 seek=16384 bs=512 conv=sync if used with image tree blob. Nice thing is that if new u-boot hangs or does not boot I can just short pin 23-25 to boot from SD card and try again. Since I have an 8Mb flash I would really like to bake in m.2 to SATA drivers - for ASM1166 in my case. Any pointers are welcome. DeMo