usual user
Members-
Posts
523 -
Joined
-
Last visited
Content Type
Forums
Store
Crowdfunding
Applications
Events
Raffles
Community Map
Everything posted by usual user
-

boot from nvme, install via armbian-install ?
usual user replied to H_Berger's topic in Orange Pi 5 Plus
Exactly Since I don't know the build, I can't make any concrete statements about it. It is also not possible under any circumstances, as the access procedures are far too complex to be meaningfully encoded in the MASK-ROM. As firmware devices, only SPI flash, MMC (eMMC, SD card), and USB with a proprietary protocol are available. This is correct. I just quickly built this version out of curiosity. I was just about to provide the binary artifacts when I quickly took a look at the schematic of your device. If I am not misinterpreting the schematic, your device only allows the fixed SPI-MMC-USB sequence and the forced immediate proprietary USB device. This means that you cannot execute the firmware completely from the microSD card, for example, if there is still a valid firmware signature in a device (SPI, eMMC) that is higher up in the priority list. It is therefore essential that you are familiar with the USB recovery procedure (MASK-ROM-MODE), in case something goes wrong during the firmware experiments with the higher prioritized devices (SPI, eMMC). -

boot from nvme, install via armbian-install ?
usual user replied to H_Berger's topic in Orange Pi 5 Plus
You are running with a broken firmware: Your version is also quite outdated: A current firmware log looks like this: -
FWIW rkvdec will be out of staging in 6.17 Be prepared to forward-port existing out-of-tree patches. cedrus has not seen much movement since a long time It can therefore be assumed that all necessary out-of-tree modifications from the past must be applied even with the latest kernel version. Since no mainline developments have taken place, no forward porting should be necessary.
-
It leaves the device with an intact file system. The corrupted file system structure has likely been restored by rolling back the journal during the automatic file system check of the unmounted file system at system startup. But the data loss is permanent. There is a reason why UPS systems exist.
-
I don't know your plans for how things are supposed to proceed. But if you plan to continue using my firmware build, I would suggest transferring it to the SPI flash, provided you are not wanted to use any other firmware in there. - This relieves you from having to pay attention to restoring my firmware build when changing an image. - You have two firmware versions available to you, between which you can switch with the SPI-MMC boot switch. - Even without the eMMC module, you can boot an OS from another connected storage device. - The U-Boot console is also available with an HDMI monitor and a USB keyboard and can be used for analysis in the event of startup problems. Of course, it is also used to select various boot options if autoboot is interrupted.
-
Use: dd bs=512 seek=1 conv=notrunc,fsync if=odroid-n2/u-boot-meson.bin of=/dev/${entire-device-to-be-used} as outlined in the referenced post to replace the existing firmware on the eMMC. Firmare is residing outside of partition layout structures so you can only write it by absolute access.
-
Certainly, but I don't know if anyone has taken the effort to integrate a current version so far. The mainline U-Boot project always provides the source codes for the latest versions. You can build it by yourself with the Armbian build framework, or use my build for a quick test.
-
The log is telling that the firmware can't operate the eMMC: Furthermore, the alternatively attempted BOOTP and PXE boot are also unsuccessful because it seems that a server is found, but the necessary bootflow is not configured correctly. As you are running a quite dated U-Boot, maybe using a cureent release has better support for the eMMC.
-
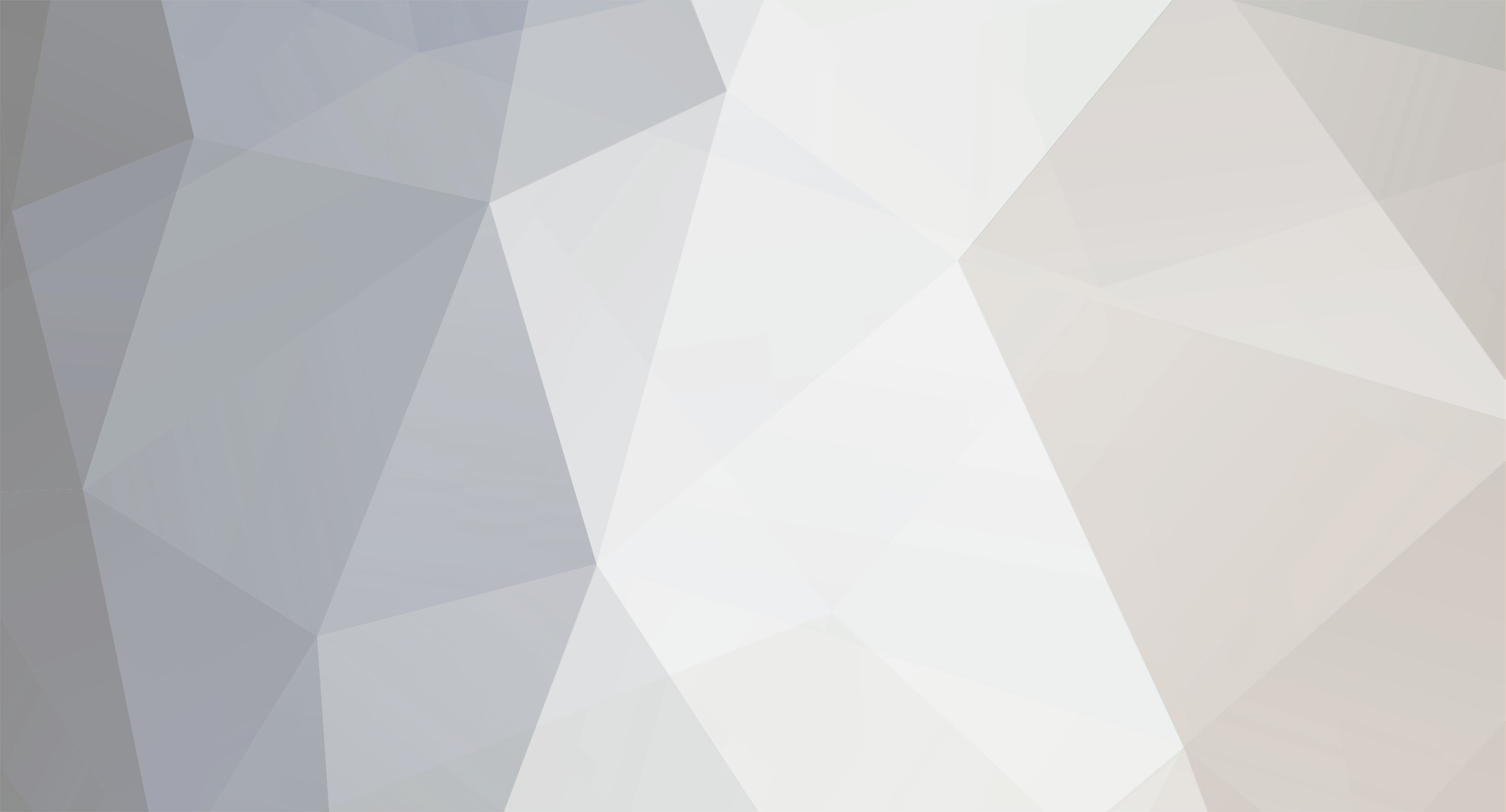
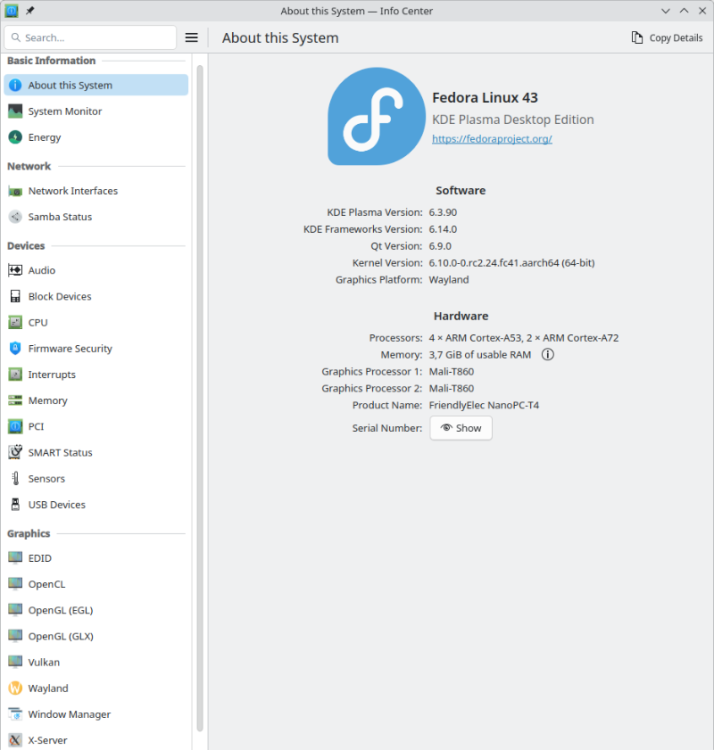
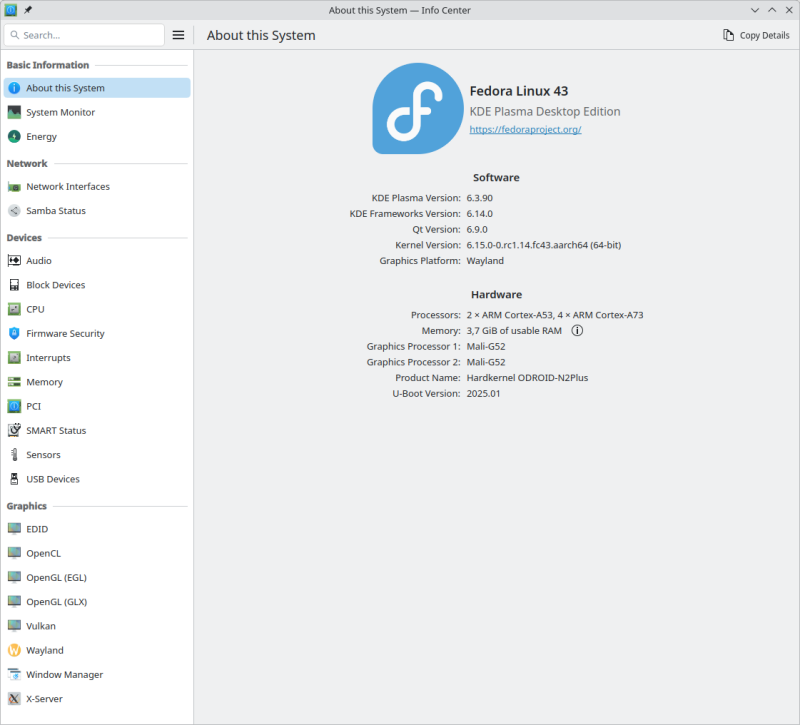
My NanoPC-T4 is still alive: For a quick test, I used my NVME with my latest OS, which usually powers a different SBC: Please do not let it bother you that the NanoPC-T4 uses an outdated kernel to run the OS. This is due to my negligence in building the current kernel without the necessary hacks needed for proper HDMI functionality. Some of the hacks have now been proper implemented in mainline, while others are still in flight. Until this process is completed, I have decided out of laziness to temporarily use an outdated kernel, as I do not miss any functionalities that a current kernel could provide me. My status LED is not blinking at boot at all. To debug boot problems, blinking LEDs are the worst possible option. Only proper console logs are of value. During OS runtime, it is configured as an HDD LED to indicate access to the microSD, as this is important information for when it is safe to remove it. I am still running my firmware from the microSD, again out of laziness to copy it to the eMMC. But any of nessesary support for the NanoPC-T4 is availabe and maybe some boring day or some spezial demand let me revisit to configure it properly. Until then, the bitrottining configuration is sufficient to serve more or less as an always-on terminal server for several USB serial adapters, which provide me with console access to my other SBCs if necessary.
-

Odroid m1 Won't boot on recent images in armbian download section
usual user replied to Mickynuts's topic in Odroid M1
EXIT to the U-Boot console and report the output of the following command: bootflow scan -l nvme I don't know what the armbian-install does, but does it make a difference if you dd the same unmodified image to the NVME as you do to the microSD? -

Odroid m1 Won't boot on recent images in armbian download section
usual user replied to Mickynuts's topic in Odroid M1
This one. -

Odroid M1: USB disk not detected after kernel upgrade 6.6.63->6.12.9
usual user replied to rmrf's topic in Rockchip
Ok, moved on to 6.14-rc1. No regressions were observed, only current fixes were applied, and new features were enabled. It may take some time for some of the fixes to trickle into new stable releases, but the new features are never officially backported. Moved on to 6.15-rc1 (boot-analyze-odroid-m1.pdf). No regressions were observed, only current fixes were applied, and new features were enabled. -

Odroid m1 Won't boot on recent images in armbian download section
usual user replied to Mickynuts's topic in Odroid M1
Ok, judging by your information, the regression takes place during the transition from U-Boot 2024.04 to 2024.07. Since mainline U-Boot works perfect for me up to until 2025.01, it must be because of how it's built or what additional patches are applied. Since it cannot be ruled out that it is due to a incompatible bootflow, it may be interesting to try it with my build. If this also fails, it is possible to get more information from the HDMI output, even if access to the serial console is not available. For the test it is perfectly sufficient to start the firmware from a prepared microSD card via RCY button. The existing setup can stay completely unchanged. -

Odroid M1: USB disk not detected after kernel upgrade 6.6.63->6.12.9
usual user replied to rmrf's topic in Rockchip
For me USB works as expected: I don't have any usbstoragequirks in place because my storage devices have controllers with properly working UAS support. I'm currently at 6.13-rc1 and will stay there at least for another two weeks. -
But I'm grateful that it also works for me with pure U-boot:
-
I'm currently at: # uname -a Linux micro-015 6.13.0-0.rc1.20241204gitfeffde684ac2.17.fc42.aarch64 #1 SMP PREEMPT_DYNAMIC Sat Dec 7 11:18:10 CET 2024 aarch64 GNU/Linux And with better wired up in DTB I get:
-
Works for me as for @rmrf. iperf3 -c ... [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-10.00 sec 1.10 GBytes 942 Mbits/sec 0 sender [ 5] 0.00-10.01 sec 1.09 GBytes 938 Mbits/sec receiver iperf3 -R -c ... [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-10.00 sec 412 MBytes 345 Mbits/sec 485 sender [ 5] 0.00-10.00 sec 410 MBytes 344 Mbits/sec receiver
-

Odroid m1 Won't boot on recent images in armbian download section
usual user replied to Mickynuts's topic in Odroid M1
Ok, then no further action needs to be taken and your solution can be used by others in the future. I also don't need any other firmware because my current one works according to my needs. And for an update, I know how to build and debug it if necessary. In the meantime, I've moved to 2025.01 with HDMI support enabled, so I no longer need the serial console to interact with the firmware. And boot menus easily allow the free choice of which option should currently be booted. -

Odroid m1 Won't boot on recent images in armbian download section
usual user replied to Mickynuts's topic in Odroid M1
To get help, you have to provide proper logs. In case of boot problems, these are serial console logs. https://debug.armbian.de -
Out of curiosity, I played around a bit with the sources offered. The overlay compiled from the spi-ili9341-tft.dts source cannot be applied statically to the base DTB. It seems to have something to do with the externally used labels. Unfortunately, my DTC package is currently in FTBFS condition and I can't investigate the cause further at the moment. I have therefore rewritten the overlay in absolute path notation. I used the given properties for this. I can't make a statement about their correctness, because I don't have a complete circuit diagram or any necessary data sheets at hand. I'm not particularly familiar with the Allwinner devicetree binding documentation, but as far as I can tell, the properties, when applied to the base DTB statically, are compliant. If you want, you can run the attached DTB with your device. All components are already statically applied, so you should disable any other dynamically applied overlays. I would be interested in the "/sys/kernel/debug/gpio" content. sun4i-a10-pcduino2.dtb
-
Allready landed in mainline, you get the fix out-of-the-box since v6.11-rc3.
-

Bricked Orange Pi 4 LTS after moving image from SD card to emmc
usual user replied to UmutU123's topic in Rockchip
This says that the necessary short circuit was not present when the MaskRom code scanned for boot devices. The short circuit must be ensured before the power supply is switched on, and must be maintained until a few seconds later. The procedure is a three-handed job. One hand fixes the PCB, one hand holds the tweezers, and one hand switches on the power supply. This can only be reliably ensured with a shelf holder who uses Pogo pinns. IMHO a bad board design for a tinker device. A push button or at least holes for a plug contact to connect a proper switch if necessary would be the better solution. Be grateful to your board designer. -

Bricked Orange Pi 4 LTS after moving image from SD card to emmc
usual user replied to UmutU123's topic in Rockchip
Since the "upgrade button" is only software readable, and the firmware (U-Boot) that does it is corrupt, only this method remains. In MaskRom_mode I would first delete the corrupt firmware in the eMMC, so that the firmware loading falls back to the microSD card. This allows different firmware variants to be tested without having to use the clunky method to get into the MaskRom_mode. Then I would prepare a microSD card with supposedly suitable firmware and boot the device with it. The function can be verified looking at the serial console output. Once a suitable firmware has been identified, I would add an OS image to the microSD card to evaluate the full functionality. It may be possible to speed up the procedure if a complete image with suitable integrated firmware is already available. Finally, if necessary, the firmware can be placed in the eMMC again.